GE Additive appoints Alexander Schmitz as CEO
- Experienced executive joins mid-January 2023, as GE Additive enters next phase of growth and transformation
- Based in Munich, Schmitz reports into Riccardo Procacci who takes on expanded role at GE Aerospace
CINCINNATI, Ohio—December 15, 2022—GE (NYSE:GE) announced today that Alexander Schmitz has been appointed as CEO of GE Additive, effective January 16, 2023. Based in Munich, Germany, Schmitz will report into GE Additive’s current chief executive, Riccardo Procacci, who takes on an expanded leadership role at GE Aerospace.
Schmitz brings extensive experience in operations, product development, manufacturing, and leading global teams. He was most recently CEO of FlexLink and previously held senior leadership and engineering positions during a 20-year career at Bosch. A mechanical engineer, Schmitz is a graduate of Aachen University, in Germany.
“I’m thrilled to be joining GE Additive as it starts its next phase of growth and transformation. I look forward to meeting the team and our customers in the new year,” said Alexander Schmitz.
“GE Additive continues to be a strategic business for GE Aerospace,” said Riccardo Procacci. “I look forward to working with Alexander and continuing to work with the GE Additive leadership team and our customers as they deploy additive, at scale, across their businesses and industries.”


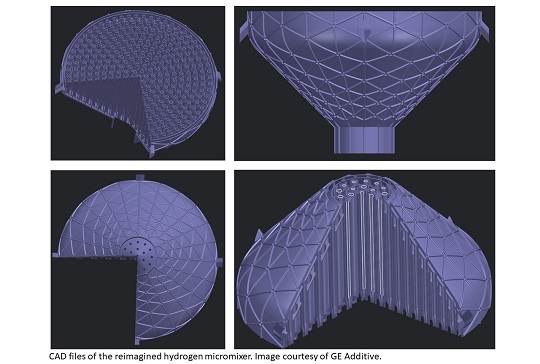
Shell International B.V. and GE Additive unveiled the results of a joint design and engineering project – an additively manufactured oxygen hydrogen micromixer.
CINCINNATI, OH – 18 November 2022 – During formnext 2022, the global additive manufacturing event, Shell International B.V. and GE Additive unveiled the results of a joint design and engineering project – an additively manufactured oxygen hydrogen micromixer. This complex, non-functional demonstration part was printed in nickel alloy 718 on a GE Additive Concept Laser M Line system, installed at Shell’s 3D Printing CoE and Workshop, part of the company’s Energy Transition Campus Amsterdam (ETCA) in the Netherlands.
Shell operates a leading 3D printing facility at ETCA in proximity to its scientists and partner companies to leverage additive manufacturing to prototype, as well as print functional parts. Having its own printing capability grants Shell’s R&D department the freedom and speed to create novel parts not available in the market and solve new technical challenges in support of the energy transition.
Joost Kroon, an additive technology subject matter expert at Shell, explains, “We really wanted to put the M Line through its paces and test it to its limits. Working with the GE Additive team we agreed to apply additive technology to reimagine a large, complex part, incorporating channels that would be difficult to manufacture conventionally. Working on an oxygen hydrogen micromixer aligns well with our companies’ strategies to play a positive role in the energy transition.”
Taking Inspiration from Geometry in Nature
Sonali Sonawane Thakker, a lead design engineer at GE Additive’s AddWorks team based in Munich, was tasked with researching, designing and iterating the final design on display at formnext. Her mission was to design a part that was large and complex and incorporated channels for hydrogen and compressed oxygen. Sonawane Thakker was able to deploy the design freedoms that additive technology affords to rethink the structure and the shape of the part.
“Once we had settled on a part, our preliminary research showed that existing micromixers – also known as hydrogen-oxygen burners – are typically cylindrical, when conventionally manufactured, to accommodate the complex layout of tanks, pipes and nozzles. For additional complexity we chose a large conical design and also moved from a flat to a curved structure with an ISO grid to increase the overall strength, rather than a customary flat one.”
Sonawane Thakker sought inspiration from geometries and symmetry in the natural world, in particular the Fibonacci sequence replicated in flowers and petals.
“With over 330 individual nozzles to incorporate in a circular pattern, I took inspiration from the ways pollen grains form in a flower head. The curved wall and the conical shape also reflect the shape of a petal,” she added.
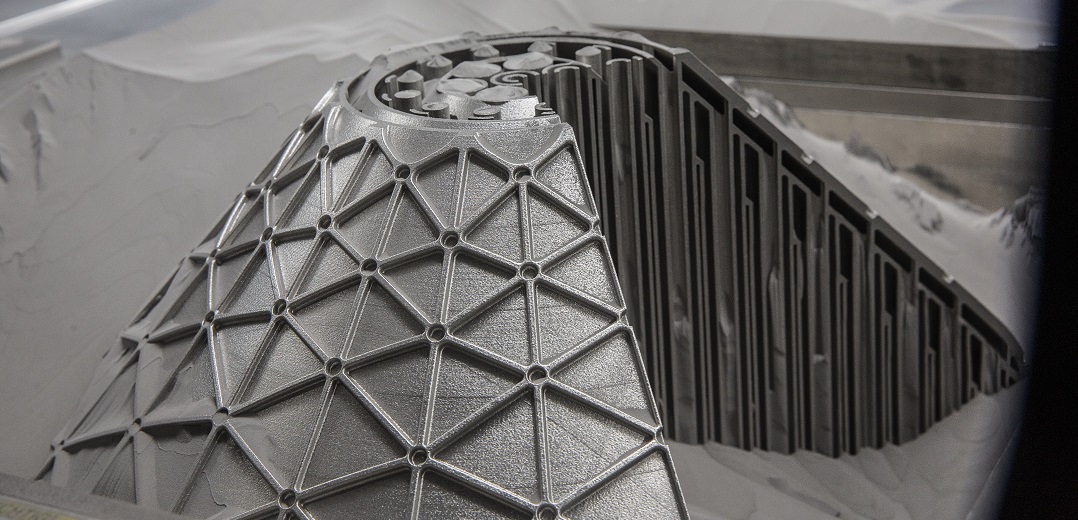
Build & post-processing
Following feasibility reviews and iterations by Shell and GE Additive teams, the design and dimensions of the reimagined part were finalized, and nickel alloy 718 was chosen as the material for the build.
Dimension of the part:
Height: ~296 mm
Diameter: 484 mm
Other: X ~ 429 mm Y ~490 mm
The build preparation and printing of the part on the M Line was overseen by Lisa Kieft-Lenders, team lead, and Dennis Boon, a technician at the Shell 3D Printing Center of Excellence and Workshop.
“We have been involved in the project from the outset and have therefore been particularly close to this build and invested in its success. Given this is one of, if not the largest and most complex part built on an M Line so far, we’ve remained in close contact with the GE Additive team in Munich and were supported on the ground here in Amsterdam by their local field service engineers. After some adaptions at the start, the build ran smoothly over nine days,” said Kieft-Leenders.
Post processing was also completed at the Shell facility, and this was made easier through inclusion of powder removal holes, incorporated by Sonawane Thakker during the design phase. The part was completed in early November and sent to GE Additive’s booth at formnext. Following the event, the micromixer will be returned and put on display at Shell’s ECTA.
“We are confident in the M Line’s ability to perform. Indeed, we grasp every opportunity to test it to its limits with both hands. I cannot underestimate the power of collaboration and problem solving during this project. It has brought together some great additive minds and the end result is not only visually stunning, but it is also substantial in size and complexity and equally strong,” said Rob Dean, GE Additive’s AddWorks leader in EMEA.
About GE Additive
GE Additive – part of GE (NYSE: GE) is a world leader in metal additive design and manufacturing, a pioneering process that has the power and potential to transform businesses. Through our integrated offering of additive experts, advanced machines, and quality powders, we empower our customers to build innovative new products. Products that solve manufacturing challenges, improve business outcomes, and help change the world for the better. GE Additive includes additive machine brands Concept Laser and Arcam EBM, along with additive powder supplier AP&C.
About Shell
Shell is a global group of energy and petrochemical companies with more than 80,000 employees in more than 70 countries. Shell uses advanced technologies and take an innovative approach to help build a sustainable energy future. Read more about Shell’s use of Addititive Manufacturing at https://www.shell.com/energy-and-innovation/digitalisation/digital-technologies/3d-printing.html.

Industrialized additive technology delivers quality parts, at cost, at scale, safely
CINCINNATI, OH – 18 OCTOBER 2022 – GE Additive has today released more details of its Binder Jet Line and the Series 3 printer. With production deliveries expected to begin in the second half of 2023, the release of the system follows a four-year phase of customer discovery, collaboration and testing to ensure the system is ready and relevant for modern, high-volume, serial production environments.
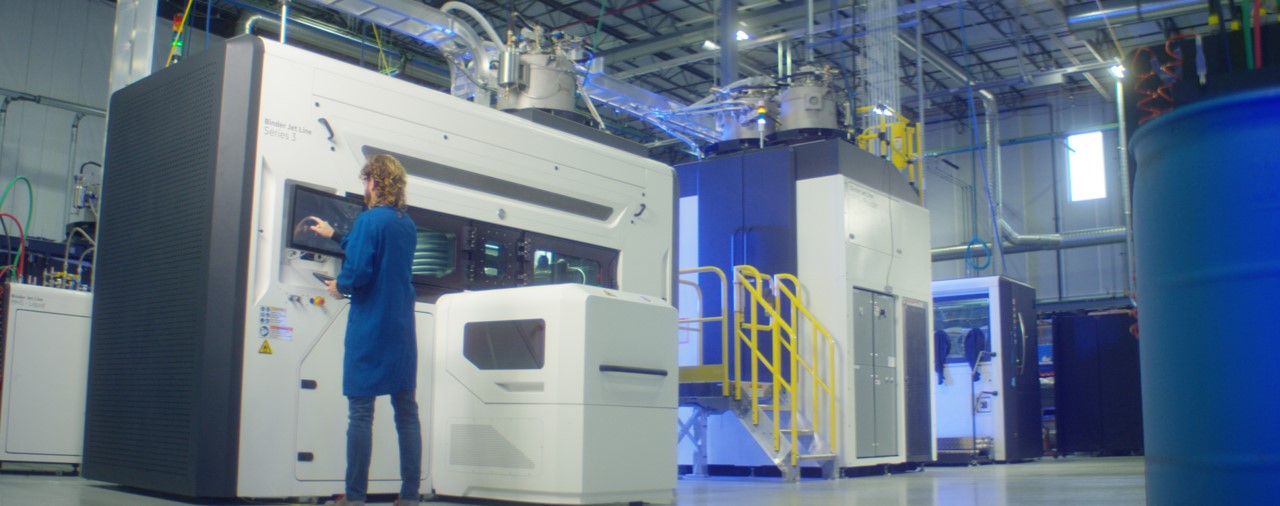

“In addition to a tangible business model, customers in fast-paced, high-volume manufacturing environments who are considering industrial-scale additive deployments also need to demonstrate positive financial and productivity impact, as quickly as possible. Customers shouldn’t have to reconfigure and tweak machines once they have been installed on their shop floor,” said Josh Mook, chief engineer and innovation leader at GE Additive.
“We remain focused on only bringing technology solutions to market when they are ready, and can help our customers demonstrate return on investment and total cost of ownership. That is certainly the case with our new Binder Jet Line and the Series 3, which is reliable, safe, and meets their needs today and tomorrow,” he added.
Customer centric innovation
Over the past four years a select group of strategic customer partners have contributed to the development of the GE Additive Binder Jet technology platform. Core to this development and knowledge, sharing work remains a mutual commitment to formally identify, design and productionize specific applications at cost, quality, at needed scale, safely.
Quality
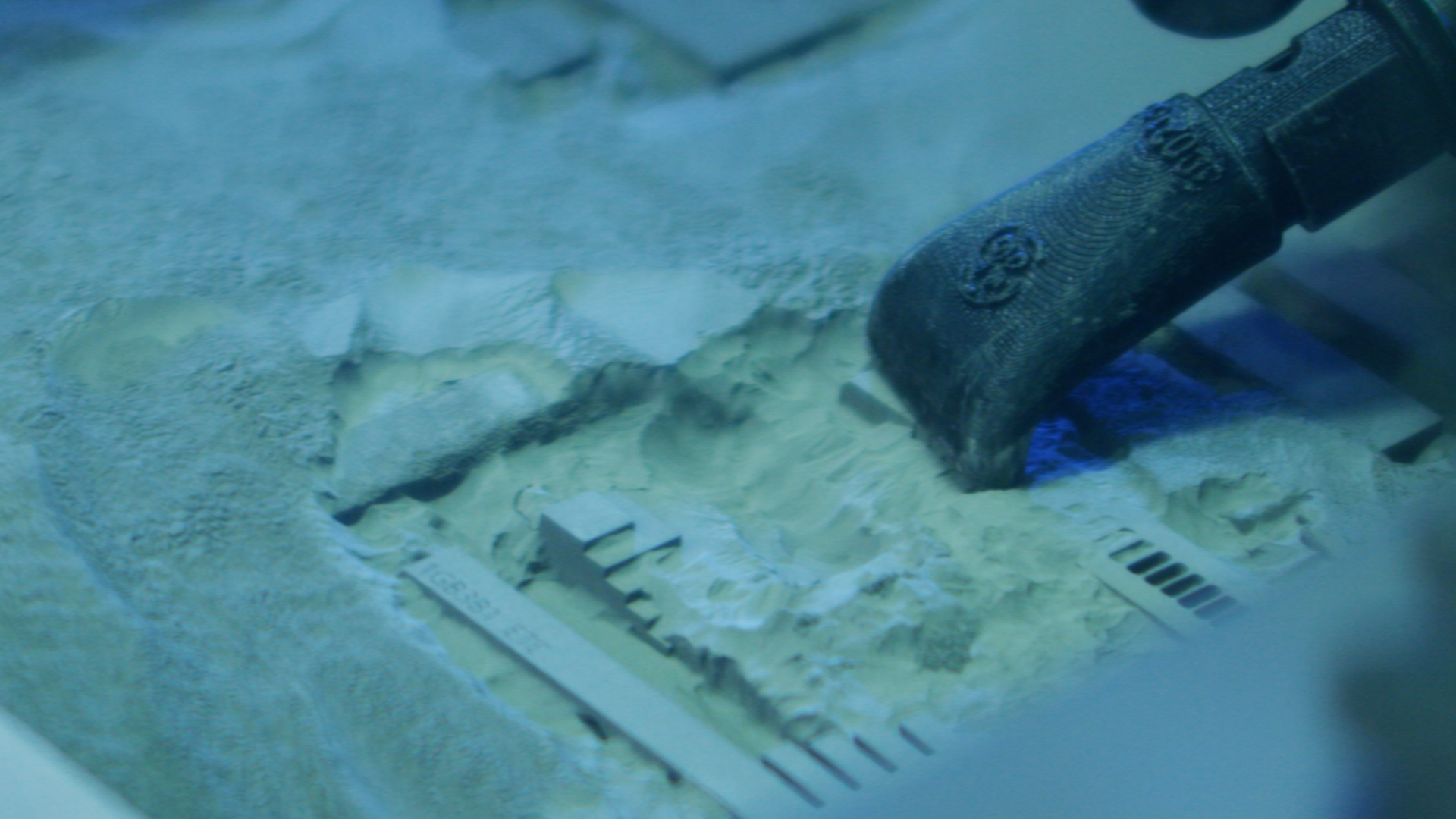
The Binder Jet Line Series 3 can additively manufacture complex, small and large parts both – repeatably and reliably, with outstanding material properties that exceed casting equivalents with achievable through-hole diameters and wall thicknesses less than 500 μm. GE’s Binder Jet technology has regularly proven the ability to successfully print and sinter large parts which meet dimensional and feature resolution tolerances for production, with demonstrated capability in (but not limited to) parts up to 25 kg in stainless steel, and no known limitations on maximum wall thickness.
The Binder Jet Line also enables the user to:
- De-powder intricate parts without destroying fine features, enabled by GE’s proprietary binder systems
- Sinter parts within the desired tolerances, enabled in part by GE Additive’s Amp software’s distortion prediction and compensation capability
- Develop casting equivalent or better, high-quality parts much faster than traditional methods
- Print and sinter parts with low surface roughness
Cost
As GE Additive strives to make industrial metal additive manufacturing an economical process, $/cc is a critical driver of the Binder Jet Line. The further the cost of a final part can be driven down, the more application space is available for the technology.
Part of those calculations include cost comparisons to conventional manufacturing technologies, in terms of tolerances and cost, from incoming raw material, to the final part in hand (total cost of ownership—not just the machine).
Other cost efficiency benefits include:
- Less spent on raw materials by recycling unused powder and leveraging less expensive material vs. other powder bed technologies
- Open space for new applications and innovation
- Utilization of the entire build box, top to bottom, edge to edge, with no need for supports
- Ability to introduce new innovative parts otherwise too costly or difficult to manufacture with conventional or other existing additive technologies
Scale
GE’s Binder Jet Line offers high overall equipment effectiveness (OEE), automation readiness, predictive distortion and compensation, and material properties that meet and exceed industry standards. All of these come together with the goal of lowest total cost of ownership for metal additive production.
Based on input from customers and partners during the technology development phase, GE Additive is focused on enabling the eventual deployment of 40, 50, 100+ machine installations that will drive repeatable process quality, while minimizing operator contact with equipment and materials.
Other scale benefits include:
- Ability to print up to 100X faster than other additive manufacturing modalities
- Automation-ready technology that drives high productivity
- Process and hardware designed to optimize Takt times
- Seamless industrialization and integration into factory cells
Safety
The Binder Jet Line can be installed and operated without hazard zoning required and has been designed for minimal operator contact with the system and metal powders.
The system will be UL listed and CE certified, has a 100% inert and sealed environment, fully closed loop powder-free exposure and is designed for compatibility with reactive and flammable powder and binders.
Other safety benefits include:
- Zero operator powder exposure for powder load and operation
- Fully independent and real-time safety system on-board constantly monitoring machine conditions
- Real-time OPC UA data streaming for integration into factory MES and safety systems

Developed by additive users for additive users
“Fast-tracking solutions and bringing them to market too soon is not a sound strategy and is often the reason machines end up gathering dust in R&D labs. During the Series 3 and Binder Jet Line’s development phase, we sought out customers who could give us honest, real-world insights from their high-volume manufacturing environments. We have taken their insights to complement our hands-on knowledge and experience of scaling additive production,” said Brian Birkmeyer, product line leader for Binder Jet at GE Additive.
“The result is a modern, modular industrialized additive system – developed by additive users for additive users – that delivers quality parts, at cost, at scale and safely,” he added.
-ends-
About GE Additive
GE Additive – part of GE (NYSE: GE) is a world leader in metal additive design and manufacturing, a pioneering process that has the power and potential to transform businesses. Through our integrated offering of additive experts, advanced machines, and quality powders, we empower our customers to build innovative new products. Products that solve manufacturing challenges, improve business outcomes, and help change the world for the better. GE Additive includes additive machine brands Concept Laser and Arcam EBM, along with additive powder supplier AP&C.


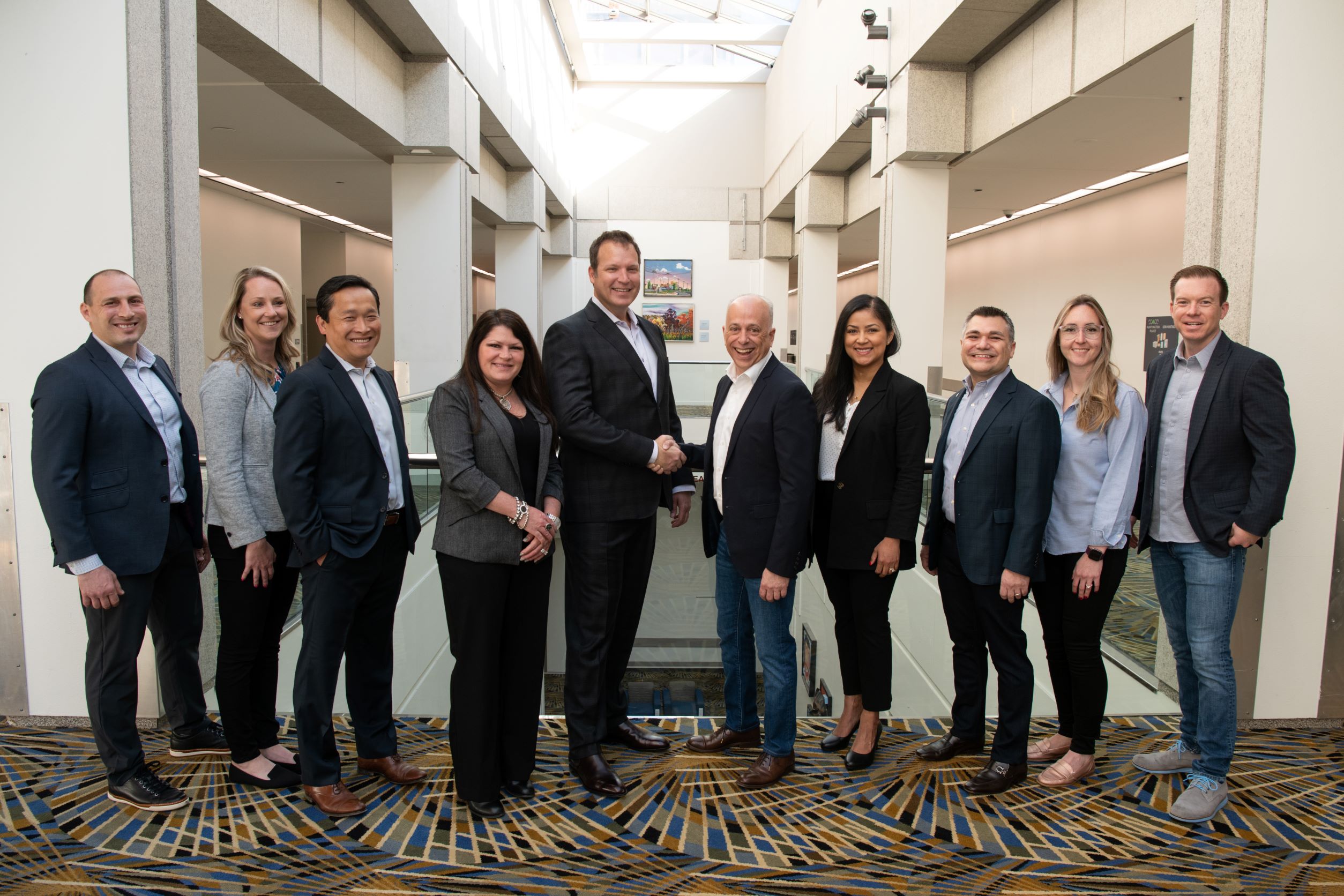
Following last month’s announcement with Orchid Orthopedic Solutions, we caught up with our colleagues Lauren Thompson and Neil Siddons and Orchid’s Josh Pang and Kristie West to discuss the agreement and immediate next steps.
Following last month’s announcement with Orchid Orthopedic Solutions, we caught up with our colleagues Lauren Thompson and Neil Siddons and Orchid’s Josh Pang and Kristie West to discuss the agreement and immediate next steps.

(L-R: Lauren Thompson and Neil Siddons, GE Additive; Josh Pang and Kristie West, Orchid Orthopedic Solutions)
How does additive manufacturing factor into Orchid’s business model and growth strategy?
Josh Pang (Orchid): We’re making a significant investment to enable scalability and full production support for our customers by purchasing GE Additive EBM Spectra L systems, service agreements, AP&C metal powders and GE Additive’s AddWorks consultancy services. With the addition of this capability, we will be able to serve customers through additive manufacturing, which complements the conventional manufacturing methods we will continue to offer.
How will our work together accelerate or impact Orchid’s additive strategy?
Josh: With our extensive knowledge of large-joint orthopedic manufacturing, we will be able to serve customers like never before through this new additive manufacturing capability. The EBM machines will allow Orchid to manufacture large orthopedic implants in new ways at more competitive prices without compromising quality. As therapies and devices become more complex, this new capability allows more cost-effective manufacturing to complement traditional methods.
Why did you choose EBM?
Kristie West (Orchid): GE Additive has an excellent reputation and is a market leader in the additive space. Our customers will have the assurance that we are taking an extra level of care by partnering with GE and drawing on their expertise and know-how. We chose EBM as the additive modality we want to enter with because of GE Additive's experience with this technology, the ability to print larger parts and the speed in which it performs, compared to other additive options.
How might Orchid’s customers eventually benefit from additive?
Josh: Bringing additive manufacturing with EBM means we can offer a different way of manufacturing to customers in addition to traditional manufacturing. Through this new capability, Orchid will become the destination customers have been seeking for their end-to-end manufacturing needs. Offering an additive manufacturing option will help enable our customers’ growth and help them provide better care to the healthcare professionals and patients they serve.
What orthopedic product types are best suited to EBM?
Kristie: Once installed and operational, Orchid’s fleet of Spectra L machines will allow us to manufacture large orthopedic implants – such as femoral knee components, tibia trays and acetabular cups – more competitively.
Lauren Thompson (GE Additive): As Kristie mentions, large-joint implants such as knees, hips and shoulders are well-suited to EBM because of this modality’s ability to effectively produce the desired mechanical properties and surface porosity, while providing superior productivity. With EBM, we’re able to achieve a balance, where there is less process waste, which enables lower-cost parts compared to conventional manufacturing techniques.
Why would orthopedic OEMs elect to manufacture their large-joint implants utilizing additive manufacturing technology?
Kristie: As devices increase in complexity, this new EBM additive manufacturing capability with scalable precision will allow us to provide cost-effective manufacturing of other large orthopedic joints in addition to the conventional manufacturing we will continue to offer.
Lauren: Complexity and design flexibility is nearly free. You can achieve a robust manufacturing process for similar component families, which can be more easily validated across multiple design variants, allowing for lower overall non-recurring engineering.
Why is GE Additive excited about this agreement?
Neil Siddons (GE Additive): We already have a sizeable installed base of EBM machines across the medical space today, who understand the potential that this modality brings. We’re excited to go to market together with Orchid. When we sat down with their wider team and reviewed what they wanted to produce and their ideal business case, we knew that EBM was the best solution for them, and specifically, the Spectra L. We see our collaboration as 1+1 = 3, which will demonstrate how collaboration can add value to the wider orthopedic sector.
What will the co-marketing program entail?
Neil: There’s no better way to market products and solutions than to let customers tell their story. We look forward to working with Orchid to tell theirs. Our co-marketing activities will be anchored in thought leadership and will show the potential of additive technology for the medical industry.
What gets you excited about additive, and specifically additive in the orthopedic sector?
Josh: Orchid has a legacy of making high-quality knees and hips and applying bone in-growth coatings. Bringing additive manufacturing with EBM means we can offer a different and cost-effective way of manufacturing to our customers in addition to the traditional manufacturing we will continue to offer. Through this new capability, Orchid will continue to be the destination customers have been seeking for their end-to-end manufacturing needs. Offering an additive manufacturing option will help enable our customers’ growth and help them provide better care for the healthcare professionals and patients they serve.
Lauren: The orthopedic sector, specifically, has adopted metal additive at a speed and scale like few other markets to date. As metal additive technologies continue to mature for industrial scale, I am excited to see how our orthopedic customers are harnessing the capability of the technology to define its runway within their businesses.
The day additive becomes widely accepted across multiple industries as an equivalent manufacturing technology to casting or CNCs will be the day additive has reached primetime.
To find out more about our work with Orchid, get in touch.


Rachel Riendeau, quality leader, and Frédéric Marion, product manager – metal powders at AP&C, a GE Additive company, discuss the process and benefits of ISO 17025

Q: Firstly, congratulations! We’ve previously discussed our quality system and how our state-of-the-art laboratory sits at the heart of our operations in Saint-Eustache, but what does the ISO 17025 accreditation mean for our customers?
Frédéric Marion: Indeed, it’s a great accomplishment many years in the making. This certification is one of the objectives we had set for the laboratory when we built our Saint-Eustache plant. We are still one of only a very few laboratories in Canada with this accreditation. We’re very proud of this additional milestone in AP&C’s journey; it is yet another proof point to demonstrate our team’s commitment to quality.
This added accreditation is greatly appreciated by our customers. First, at the core of an ISO 17025 accreditation is the assurance that the methods used—and therefore the results attained—are benchmarked against industry standards and consistent over time. Second, the laboratory’s independence from outside influence is reinforced within ISO 17025. This is reassuring for customers who buy our products.
Also, as AP&C’S core markets include highly regulated industries, such as medical and aerospace, testing in a certified ISO 17025 laboratory is often required. This accreditation for our internal lab allows us to have more control over testing costs and lead times and overall quality controls over our products. It will also help customers to use our powder testing service to analyze used powder and perform investigations or R&D work.
We believe that AP&C’s quality-driven attitude is a big part of our success. For us, quality is not only about complying with requirements but also about improving processes and sharing best practices. And this accreditation is only one block on our already strong quality foundation.
Q: What does the accreditation process entail with the Standards Council of Canada, or The Canadian Association for Laboratory Accreditation? And how does having ISO 17025 accreditation complement our other certifications, namely ISO 9001, AS9100 for the aerospace customers and ISO 13485 for the medical market?
Rachel Riendeau: AP&C actively prepared for this accreditation for a more than a year. Although ISO 17025 accreditation includes management requirements—like other quality certifications—and process requirements that are specific to laboratory activities, accreditation is applicable only to the tests specified in the scope. In the case of AP&C, since titanium alloys are our core products, we decided that the chemical analysis of titanium alloys would be part of our accreditation scope, as well as particle size distribution testing, by sieving and light scattering.
In preparation for this accreditation, we performed a complete gap analysis of our testing management process as well as our quality system to identify what needed to be updated to be compliant to the ISO 17025 standard. Even though AP&C’s laboratory is already managed under the umbrella of AP&C’s multiple quality management system certifications (ISO 9001, ISO 13485 [medical devices] and AS9100 [aerospace]), this accreditation puts an emphasis on robustness of controls to ensure AP&C’s laboratory operates competently and can generate valid results. It also promotes impartiality and independence from production, which is crucial to maintain the credibility and integrity of a captive laboratory. To ensure compliance to these additional requirements, procedures and instructions were reviewed or created, risk analyses of laboratory activities were conducted, and all teams involved in the laboratory processes were thoroughly trained.
Regarding the accredited testing methods, round robin (testing of a sample by multiple laboratories to determine reproducibility) and statistical analysis of our testing results were used to validate our methods and confirm the high accuracy of our testing process.
Q: Is this ISO standard primarily concerned with testing and calibration and ensuring labs consistently produce valid test results?
Frédéric: Yes. Calibration and method control through statistical analysis is a big part of this certification, but it is also important to point out that the certification is based on pre-established ASTM standards and based on the laboratory capability to reproduce results from other laboratories.
This might look simple enough; you have a method, you follow it, you make sure you get the same result as others. That’s all!
Well, not exactly. For reactive materials, like titanium, and in an industry like additive manufacturing—which has stringent requirements—we need precise control of the material properties and often need to push the understanding of the method to another level to obtain accurate results with little deviation. As an example, sometimes the availability of the proper certified reference material (CRM) can be a challenge for certain narrow chemical compositions requirements.
AP&C’s team strives to better understand and control products, and this is pushing us to improve our analysis tools. As leader in the market, we also want the full industry to gain from our knowledge. That is why we continuously share our experiences by participating in ASTM committees that review methods. This is something that we also do with additive powder specifications from ASTM and AMS. We are also involved in the creation of the upcoming NAPCAP certification for metal powder production for additive manufacturing.
Q: What does the accreditation mean from a product management perspective?
Frédéric: In short, it helps us drive better process controls. The biggest benefit is probably on the product management point of view as we can gather more reliable data on our products and then tighten the product requirements. Again, this helps our customer get consistent products that meet their production needs.
Q: How does team feel about getting the accreditation?
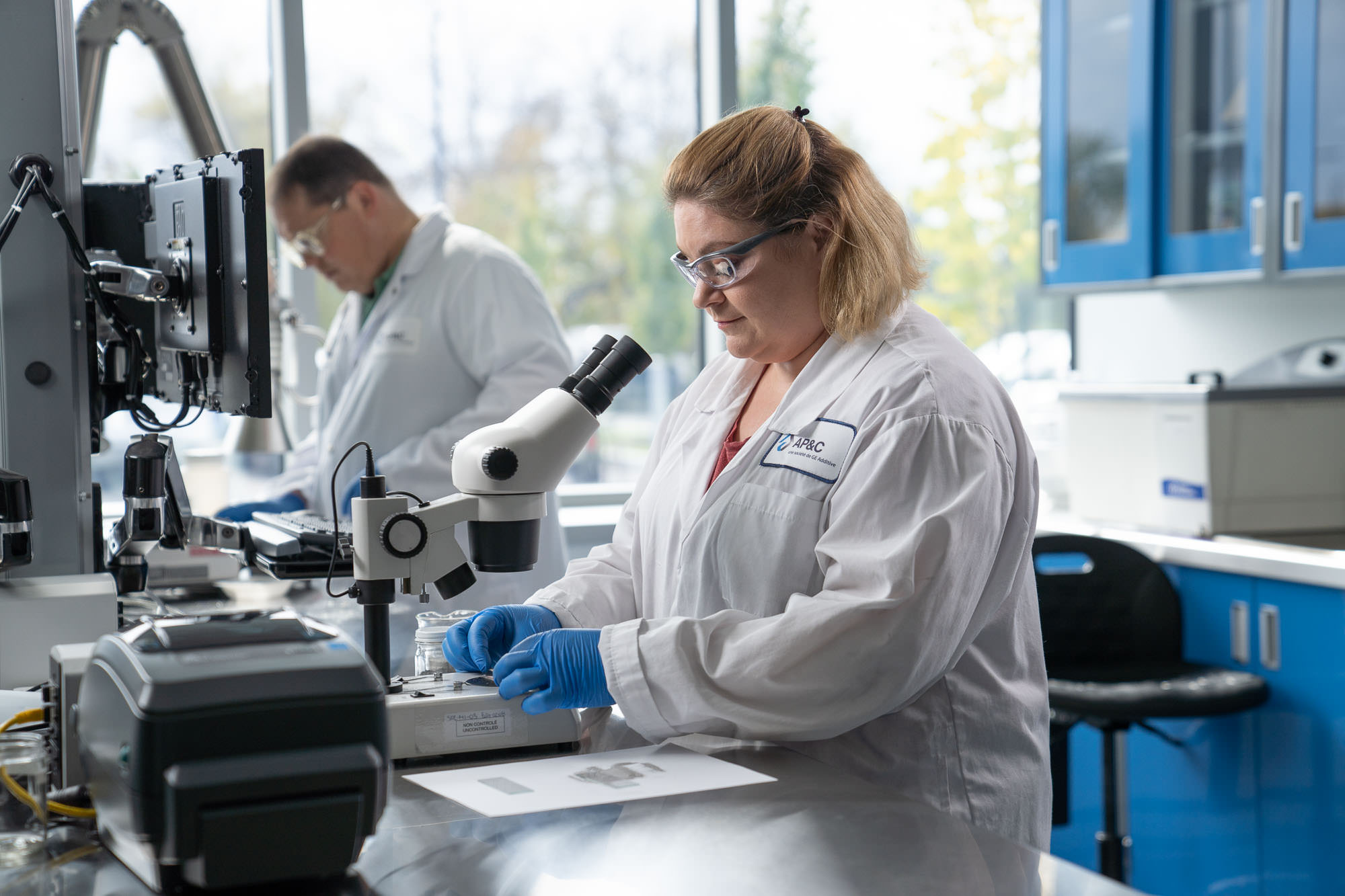
Rachel: The AP&C laboratory team is very proud of all the hard work accomplished to achieve this accreditation. They have always strived toward high quality and customer satisfaction, maintaining a high level of control in their everyday activities. This accreditation recognizes their efforts and confirms that their dedication is worth it. I would like to take this opportunity to personally thank and congratulate everyone involved in this project, a great achievement for AP&C and another step on our journey towards quality excellence.

(From left to right: AP&C laboratory team. Jean-François Archambault, Valérie Cloutier, Catherine Lavoie, Josée Hamel and Eric Beaudin)
Q: What’s next?
Frédéric: Chemical composition and particle size distribution were only the first step. Next in line will be the other powder physical properties (flow rate, apparent density, tap density, humidity, etc.). But obviously we continue to invest in our testing capabilities at AP&C and throughout our GE Additive network. From CT-scan to SEM to powder rheology, we always keep our eyes open for methods that will help our customers understand what product property drives their process performance. We also try to develop new ways to understand our great products.
To find out more about AP&C get in touch with the team here.


DETROIT, MICHIGAN – May 17, 2022 – At RAPID + TCT, GE Additive and Orchid Orthopedic Solutions (Orchid) – a global leader in the manufacture of orthopedic implants and instruments – announced they have signed a definitive agreement to continue driving the adoption of additive manufacturing to their suite of technologies through the development of electron beam melting (EBM) solutions in the medical implants sector.
Orchid will make a significant investment to enable scalability and full production support for its customers by purchasing GE Additive EBM Spectra L systems, service agreements, AP&C metal powders, and GE Additive's AddWorks consultancy services. Installation of the first machines will commence in 2022. Following machine installation and validation, Orchid expects to be ready for production in 2024 to meet its customers’ requirements.
GE Additive and Orchid are focused on joint co-marketing activities aimed at driving further awareness of EBM technology in 3D metal printed large joint orthopedic implants.
“We are thrilled to collaborate with GE Additive to bring additive manufacturing capabilities to our customers,” said Nate Folkert, Chief Executive Officer, Orchid. “GE Additive has an excellent reputation and is a market leader in the additive space. Together with our extensive knowledge of large joint orthopedic manufacturing, we will be able to serve customers like never before. They will have the assurance that we are taking an extra level of care by partnering with GE Additive. I look forward to seeing Orchid drive continued additive manufacturing innovation as a result of this Agreement,” he added.
“I am honored that Orchid has put their confidence and trust in GE’s additive expertise, at such an important juncture in their metal AM journey. I look forward to our teams building a long-term relationship over the coming years,” said Riccardo Procacci, President & CEO, GE Additive. “I have personal experience overseeing the deployment of a large fleet of industrialized EBM machines for precise scalable AM production at GE Aviation’s Avio Aero business, so I look forward to getting to know the Orchid team and sharing some of my insights. I also continue to be amazed at how our existing medical customers and orthopedic community are using metal additive to innovate and drive better and often personalized outcomes for patients,” he added.
Manufacturing Larger Parts Competitively
Once installed and operational, Orchid’s fleet of Spectra L machines will allow it to manufacture large orthopedic implants, such as complete knee components and acetabular cups and more competitively. As devices increase in complexity, this new EBM additive manufacturing capability with scalable precision allows cost-effective manufacturing to complement conventional methods.
The Arcam EBM Spectra L allows for the mass production of parts by providing the ability to tightly stack parts without compromising on quality. The improved melt process results in consistent material properties for thin and bulky geometries. Some of the key features:
• Enhanced part quality, with improved surface finish and improved material properties.
• Reduced cost per part due to increased build speed, the largest EBM build volume, and the ability to tightly stack parts
• Integrated system architecture, with standardized IoT interface, data analytics for machine health monitoring and the new Powder Recovery Station, PRS 30.
- ends -
About Orchid Orthopedic Solutions
Orchid is a world leader in orthopedic medical device solutions, providing manufacturing services globally. As a strategic partner, Orchid has the broadest portfolio in the industry, ranging from finished goods manufacturing through packaging, improving customers’ supply chains and adhering to the highest quality standards in the industry. Orchid specializes in implants, single use instruments and innovative technologies within joint reconstruction, hips, knees, spine, trauma, extremities and dental. For further information, visit www.orchid-ortho.com.
About GE Additive
GE Additive – part of GE (NYSE: GE) is a world leader in metal additive design and manufacturing, a pioneering process that has the power and potential to transform businesses. Through our integrated offering of additive experts, advanced machines, and quality powders, we empower our customers to build innovative new products. Products that solve manufacturing challenges, improve business outcomes, and help change the world for the better. GE Additive includes additive machine brands Concept Laser and Arcam EBM, along with additive powder supplier AP&C.


LICHTENFELS, GERMANY – 16 May 2022 – BEAMIT Group (BEAMIT), partly owned by SANDVIK, has invested in a GE Additive Concept Laser M Line system to meet growing demand from its aerospace and defense customers for both large format metal 3D-printed components and assistance in industrializing additive production.
This investment comes six months after Avio Aero, BEAMIT and GE Additive signed a letter of intent regarding a strategic technology collaboration. BEAMIT is a longstanding customer of GE Additive and operates a fleet of Concept Laser and Arcam EBM machines, including the Mlab, M2 and X Line platforms, as well as two Q10plus machines across its three manufacturing plants and its subsidiary PRES-X.
Demand for Larger Additive Parts
“As part of our ‘one-stop-shop’ strategy, we have continued to invest in our value chain over the past seven years and have also achieved rigorous ISO 9001, AS 9100 quality certifications and NADCAP accreditation needed to service the aerospace sector. That investment has not gone unnoticed and we continue to attract new aerospace, space and defense customers, while supporting existing customers who have already commenced their additive journey,” said Mauro Antolotti, President of BEAMIT Group.
“Today, we are seeing an increasing demand from customers for much larger, more complex parts, and in higher volumes— this is why we have invested in our first M Line system. Based on our strong and well-recognized expertise in discovering new applications for additive manufacturing, we see in the new platform M Line, combined with our full cutting edge end-to-end value chain, the key for a technological leap towards significantly increased production volumes in the near future. The BEAMIT team is ready to explore the potential of the M Line and continuously improve the industrialization process by digitally connecting the system with all the subsequent post-processing phases. We will work closely with GE Additive’s AddWorks consultants to make this development even faster,” said Andrea Scanavini, Chief Commercial Officer of BEAMIT Group.
The rise in demand for larger parts that BEAMIT is experiencing is replicated across the commercial aerospace, space and defense sectors, globally. Additive users across the aerospace supply chain continue to invest in innovation and in doing so continue to set the bar high for the deployment of increasingly mature metal additive applications. The progression in terms of complexity and volume is a reflection of the evolving sophistication of in-house additive teams, one-stop shop companies like BEAMIT with an end-to-end approach, and the wider aerospace additive ecosystem.
Enabling Industrialization Faster
This latest phase of industrialization builds on widespread success in deploying metal additive across the aerospace industry, where users are able to demonstrate tangible return-on-investment, in terms of productivity and cost-part reduction, and are now able to make a tangible business case for scaling their additive operations.
“Being closely aligned through our own activities across GE Aviation, including Avio Aero, and many other customers in aerospace, we anticipated this next wave of industrialization. For some time our common objective with BEAMIT has been to work closely together to enable their customers to make the shift to industrialization as seamless as possible, we feel now quite proud that this becomes a reality,” said Rob Dean, GE Additive’s AddWorks senior leader in Europe.
Once installed at its facility in Italy, the BEAMIT team will push the utilization of M Line to its full potential in terms of quality, productivity and driving cost out for additive production, also with the support of GE Additive’s AddWorks consultants.
The M Line has been developed for high-quality, high throughput scenarios and lends itself well to highly-regulated industries such as the aerospace and medical sectors. While it is intuitive and easy to operate, the M Line is a highly-advanced, industrialized production system that is well-suited to customers who have experienced metal additive users for many years and have already started to scale production volumes.
“Customers, like BEAMIT, recognize that GE Additive’s experience and products can help them move to serial production quicker. It’s great to see BEAMIT invest in the M Line and build on our strategic technology collaboration that will not only benefit the aerospace industry, but also the wider industrial additive community here in Europe and around the world,” said Wolfgang Lauer, product line manager – M Line, GE Additive.
Find out more about this announcement at the RAPID + TCT show in Detroit, May 17-19 at the Sandvik-BEAMIT booth (#3431) and the GE Additive booth (#2620).
- ends -
Picture above shows Andrea Scanavini, Chief Operating Officer, BEAMIT (center) with GE Additive’s Fausto Asvisio (left) and Wolfgang Lauer (right) with an M Line at GE Additive Lichtenfels.
About BEAMIT Group
BEAMIT Group has been operating Additive Manufacturing (AM) with metal powders for over 25 years and is today one of the most advanced AM service providers in the world. The company serves some of the most demanding industries, like aerospace, automotive, medical, energy, racing and industrial engineering – through its strategic positioning as a One-Stop-Shop supplier. BEAMIT Group was the first company to become a truly global AM hub, offering a fully integrated value chain. The company is an approved supplier for serial production by many leading OEMs, and holds a significant number of quality certifications, including AS/EN 9100:2018 for aerospace, IATF automotive, NADCAP accreditation for heat treatment processes and laboratories, and NADCAP accreditation for welding – additive manufacturing commodity.
In 2019, Sandvik acquired a significant stake in BEAMIT. Since then, BEAMIT Group has fully incorporated service bureau ZARE (acquired in 2020). It acquired UK-based 3T Additive Manufacturing in 2021 and holds a significant participation in PRES-X – specialized in high-end post processing for 3D printing – since 2020. The BEAMIT Group’s HQ is located in Fornovo di Taro (Parma, Italy). Today the company counts over 140 employees and close to 60 dedicated AM systems, distributed across 7 facilities in Italy and UK.
About Sandvik Additive Manufacturing
Sandvik Additive Manufacturing has a world-leading position in metal powder with the widest range of AM-alloys on the market. The company has also made sizeable investments into a wide range of AM printing technologies since 2013. Adding 160 years of leading expertise in materials technology, 75 years in post processing methods like metal cutting, sintering and heat treatment, Sandvik has well established and leading competence across the entire AM-value chain. In 2019, Sandvik acquired a significant stake in BEAMIT, a leading European-based AM service provider, and after this, the BEAMIT Group has acquired 100% of ZARE and 3T Additive Manufacturing, bringing together three leading AM service bureaus in Europe – to create one of the largest independent AM service providers in the world, serving the most demanding industries.
Sandvik AB is a high-tech and global engineering group with approximately 44,000 employees and sales of approximately 99 billion SEK in more than 150 countries (2021). The company was founded in Sweden in 1862 and is listed on the Stockholm stock exchange since 1901.
About GE Additive
GE Additive – part of GE (NYSE: GE) is a world leader in metal additive design and manufacturing, a pioneering process that has the power and potential to transform businesses. Through our integrated offering of additive experts, advanced machines, and quality powders, we empower our customers to build innovative new products. Products that solve manufacturing challenges, improve business outcomes, and help change the world for the better. GE Additive includes additive machine brands Concept Laser and Arcam EBM, along with additive powder supplier AP&C.


GE Additive product line leader Brian Birkmeyer interviews Kennametal Additive Manufacturing's general manager Jay Verellen about their partnership with GE Additive for their Binder Jet technology.

Kennametal Inc., a leading industrial technology company, is the latest member of GE Additive's Beta Partner Program. As a part of the GE Additive Program, Kennametal will further develop its Binder Jet printing capabilities in cemented tungsten carbide and scale up its end-to-end metal additive manufacturing solutions, from metal powders to 3D-printed parts and tooling.
CINCINNATI, OH – 12 May 2022 – GE Additive today announced that industrial technology leader Kennametal Inc. is the latest member of its Beta Partner Program. As part of the GE Additive Program, Kennametal will further advance its Binder Jet printing capabilities in cemented tungsten carbide as it continues to scale its end-to-end metal additive manufacturing solutions, from metal powders through to the production of 3D-printed parts and tooling.
Kennametal’s metal 3D-printed parts have already gained wide customer adoption across a variety of industries, such as oil & gas, energy, industrial processing and transportation. Kennametal will work with GE Additive to identify, design and scale specific applications for serial production on GE’s Binder Jet system, leveraging Kennametal’s proprietary cemented tungsten carbide additive materials.
Kennametal is a global leader in tungsten carbide and Stellite™ (cobalt chrome alloy) alloys recognized for their superior wear, heat and corrosion performance. Kennametal is focused on optimizing these high-performance, wear- and corrosion-resistant material families to additive platforms to produce fully finished components with complex designs, shorter lead times and improved performance not possible through traditional manufacturing. When combined with additive manufacturing, these proprietary material systems can offer a step change in wear and corrosion solutions for some of the most challenging applications.
“Customers are increasingly seeking our 3D-printed tungsten carbide and Stellite solutions to help them maximize their productivity in challenging applications when wear and corrosion resistance are critical,” said Jay Verellen, general manager, Kennametal Additive Manufacturing. “Our work with GE Additive on Binder Jet solutions will enable further scaling of our operations to meet strong customer demand—and extend our leadership in proprietary material solutions for additive.”

Customer-Centric Innovation
GE Additive continues to develop its Binder Jet solution to make additive manufacturing a reality for serial production, targeting millions of parts per year and beyond. Key to that development is ongoing, hands-on input from members of GE Additive’s Binder Jet Beta Partner Program.
“By hands-on, we don’t mean tinkering or experimenting. We work closely with our beta customers as they develop their own, real-world business cases, applications and parts. To them, it is important that our solution is not only mature and scalable but is capable, complete and aligns to their product innovation strategies and meets production volume needs,” said Brian Birkmeyer, product line leader for Binder Jet at GE Additive.
“We are honored that Kennametal, an industry leader in 3D-printed tungsten carbide, is working closely with us on the development of our Binder Jet platform. Ensuring we align with Kennametal’s production expectations and requirements is a top priority. Their longstanding expertise in materials science mirrors our own, and our team is excited to work together to deliver new and innovative solutions,” added Birkmeyer.
About Kennametal
With over 80 years as an industrial technology leader, Kennametal Inc. delivers productivity to customers through materials science, tooling and wear-resistant solutions. Customers across aerospace, earthworks, energy, general engineering and transportation turn to Kennametal to help them manufacture with precision and efficiency. Every day approximately 8,600 employees are helping customers in more than 60 countries stay competitive. Kennametal generated approximately $1.8 billion in revenues in fiscal 2021. Learn more at www.kennametal.com. Follow @Kennametal: Twitter, Instagram, Facebook, LinkedIn and YouTube.
About GE Additive
GE Additive – part of GE (NYSE: GE)– is a world leader in metal additive design and manufacturing, a pioneering process that has the power and potential to transform businesses. Through our integrated offering of additive experts, advanced machines and quality powders, we empower our customers to build innovative new products. Products that solve manufacturing challenges, improve business outcomes and help change the world for the better. GE Additive includes additive machine brands Concept Laser and Arcam EBM, along with additive powder supplier AP&C.


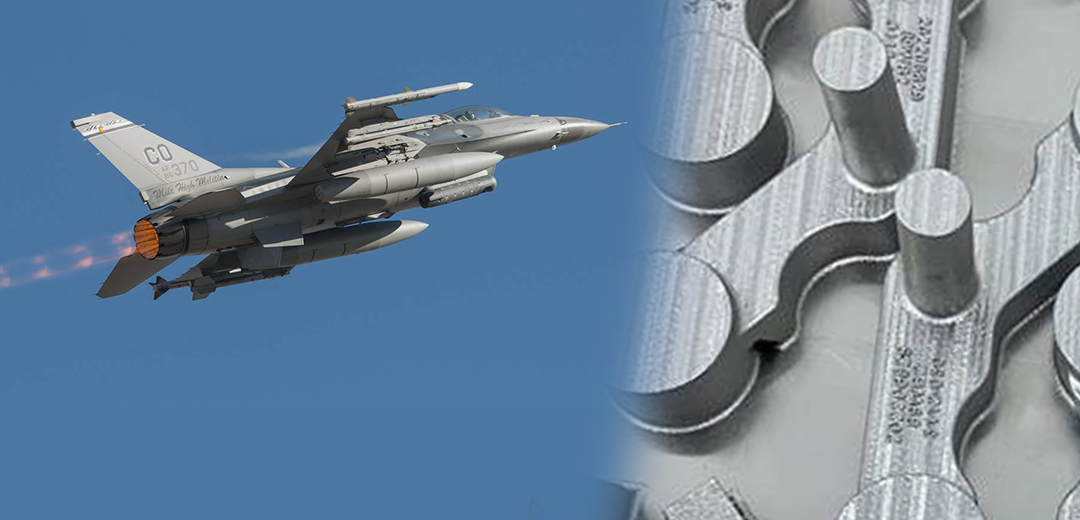
The US Air Force (USAF) and GE recently entered the third phase of its “Pacer Edge” pathfinder. Phase III has focused on 3D printing four parts that are currently obsolete: a bellcrank, gearbox seat, anti-icing valve body and a cross-shaft arm.
Cincinnati, OH – 6 May 2022 – The US Air Force (USAF) and GE recently entered the third phase of its “Pacer Edge” pathfinder. Phase III has focused on 3D printing four parts that are currently obsolete: a bellcrank, gearbox seat, anti-icing valve body and a cross-shaft arm. The first two parts, the cross-shaft arm and the bellcrank, have been successfully printed in cobalt-chrome on a fleet of M2 Series 5 system at GE Additive‘s facility in Cincinnati.
The final phase of the program over the coming years is to establish the USAF’s own metal additive production infrastructure initially at Tinker Air Force Base in Oklahoma. This capability will alleviate long lead times that currently plague the casting and forging industries.
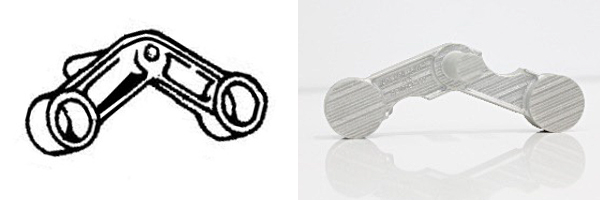
Left: A hand-drawn technical illustration of the cross-shaft arm dating from the 1960s. Image Credit: USAF
Right: The first successful development build of the cross-shaft arm was printed nine months after requirement flow down. Image Credit: GE
“Pacer Edge represents a monumental step forward in innovative partnership with industry. Through this program, our enterprise team will deliver safe and timely propulsion readiness in support of the United States warfighter,” said Mr. John Sneden, director of propulsion, USAF.
USAF is not the only entity struggling to receive their castings and forgings in a timely manner. It remains a choke point for many industries and has only been exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
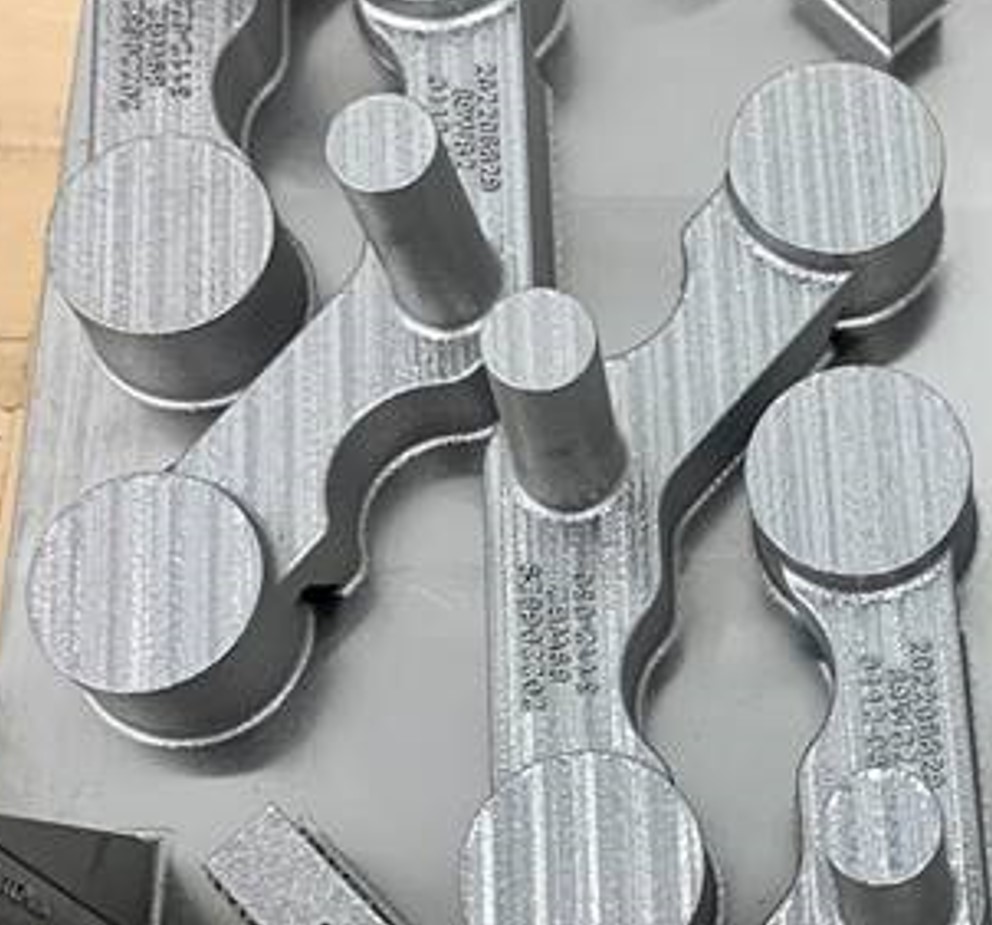

Metal 3D printed production parts for the Pacer Edge program (printed in cobalt-chrome and nickel alloy 718 on GE Additive's Concept Laser M2) nine months after requirement flow down. Image Credit: GE Additive
“Public-private initiatives like the recently announced ‘AM Forward’ initiative will also help to address DoD’s sustainment and readiness challenges head on,” said Lauren Tubesing, director of operations, military programs at GE Additive. “Strengthening U.S. supply chains, by encouraging small and medium sized manufacturers across the United States to adopt metal additive technology, will create a nationwide network of a qualified additive manufacturing supplier.”
About GE Additive
GE Additive – part of GE (NYSE: GE) is a world leader in metal additive design and manufacturing, a pioneering process that has the power and potential to transform businesses. Through our integrated offering of additive experts, advanced machines, and quality powders, we empower our customers to build innovative new products. Products that solve manufacturing challenges, improve business outcomes, and help change the world for the better. GE Additive includes additive machine brands Concept Laser and Arcam EBM, along with additive powder supplier AP&C.


