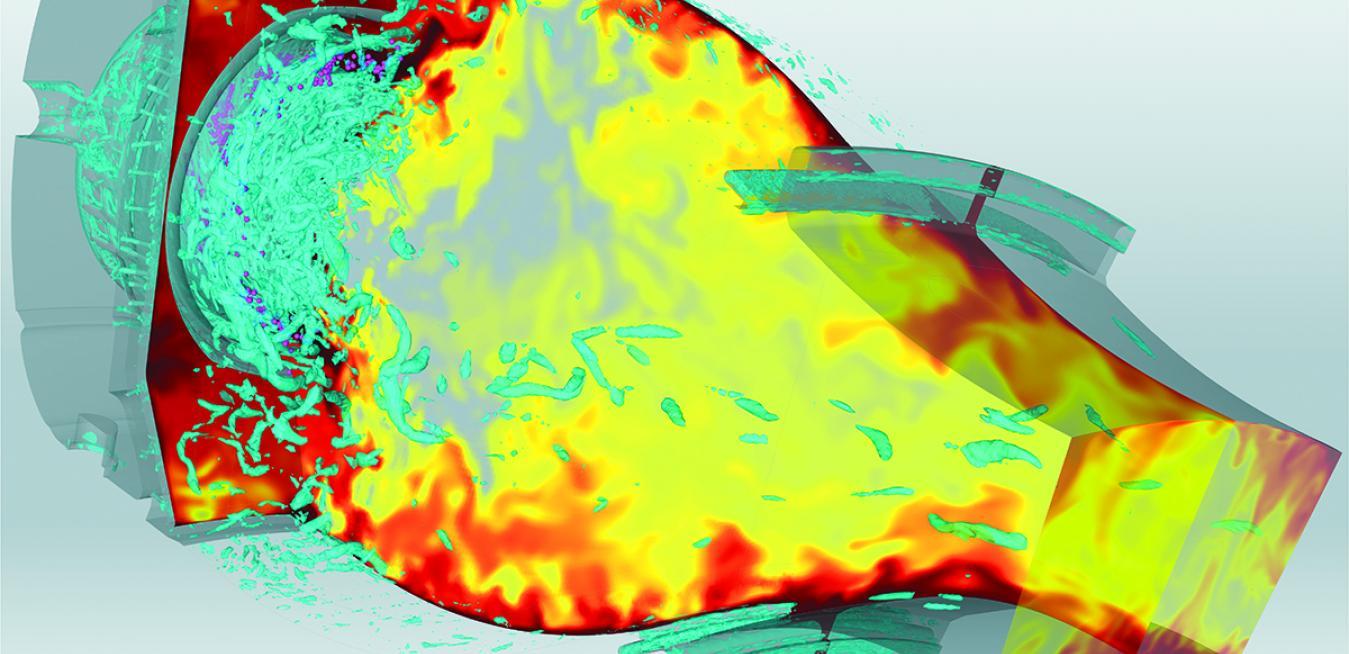
In the five decades since the first Earth Day, the world has made much progress in understanding the perils posed by climate change and finding the solutions we need. But we are far from done. The switch to electric cars alone will force us to reimagine not only how we make electricity, but also how we distribute it.
Renewables are clearly a big part of the future of energy, but so are natural gas, energy storage, hydropower and the digital grid. Other industries, like aviation, must also decarbonize to help prevent the planet from warming.
Marshall Jones knows a thing or two about beating the odds, but it’s not just because of his knack for mathematics. A model of perseverance, the laser pioneer was raised by his extended family on a duck farm but ended up laying the foundation for additive manufacturing, a new breed of technologies that allow companies to 3D-print things from metal.
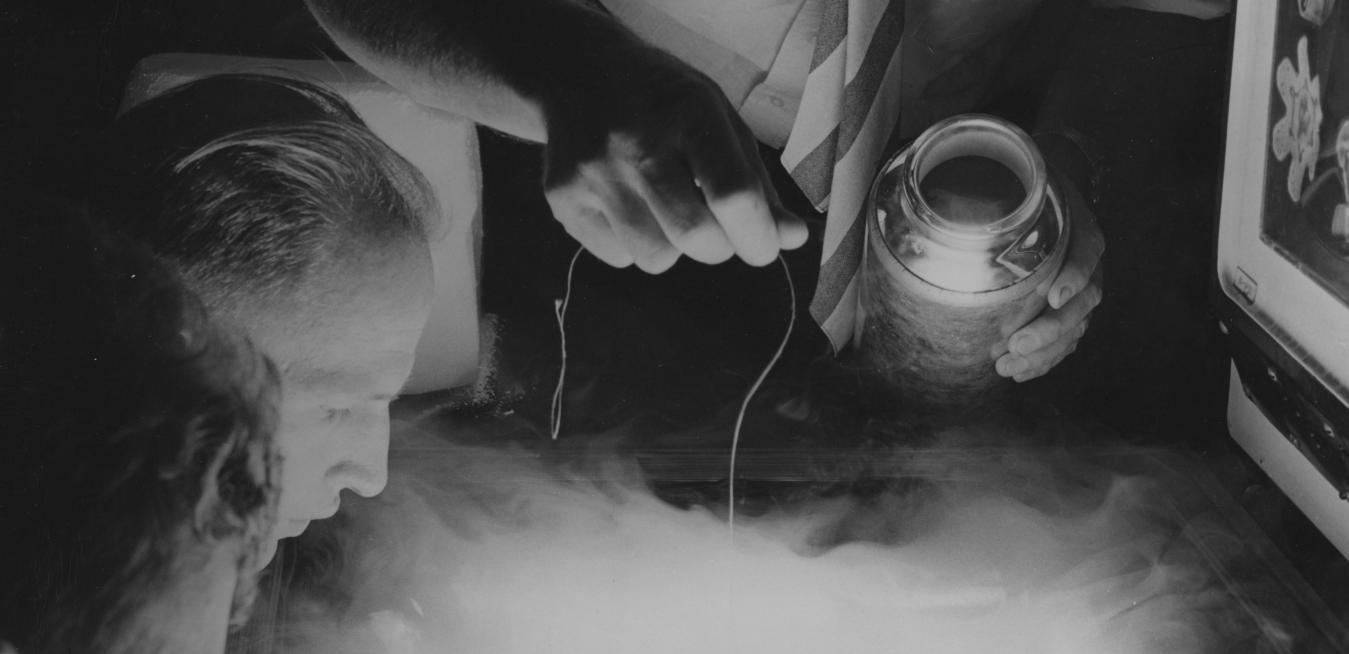
Kurt Vonnegut’s science-fiction novel “Cat’s Cradle” revolves around a tricky compound called ice-nine that can turn water solid at room temperature. Vonnegut, who worked for GE in the 1950s as an in-house journalist, came up with many beautifully outlandish plots for his best-selling books. But ice research was hitting close to his beat as well as his home.
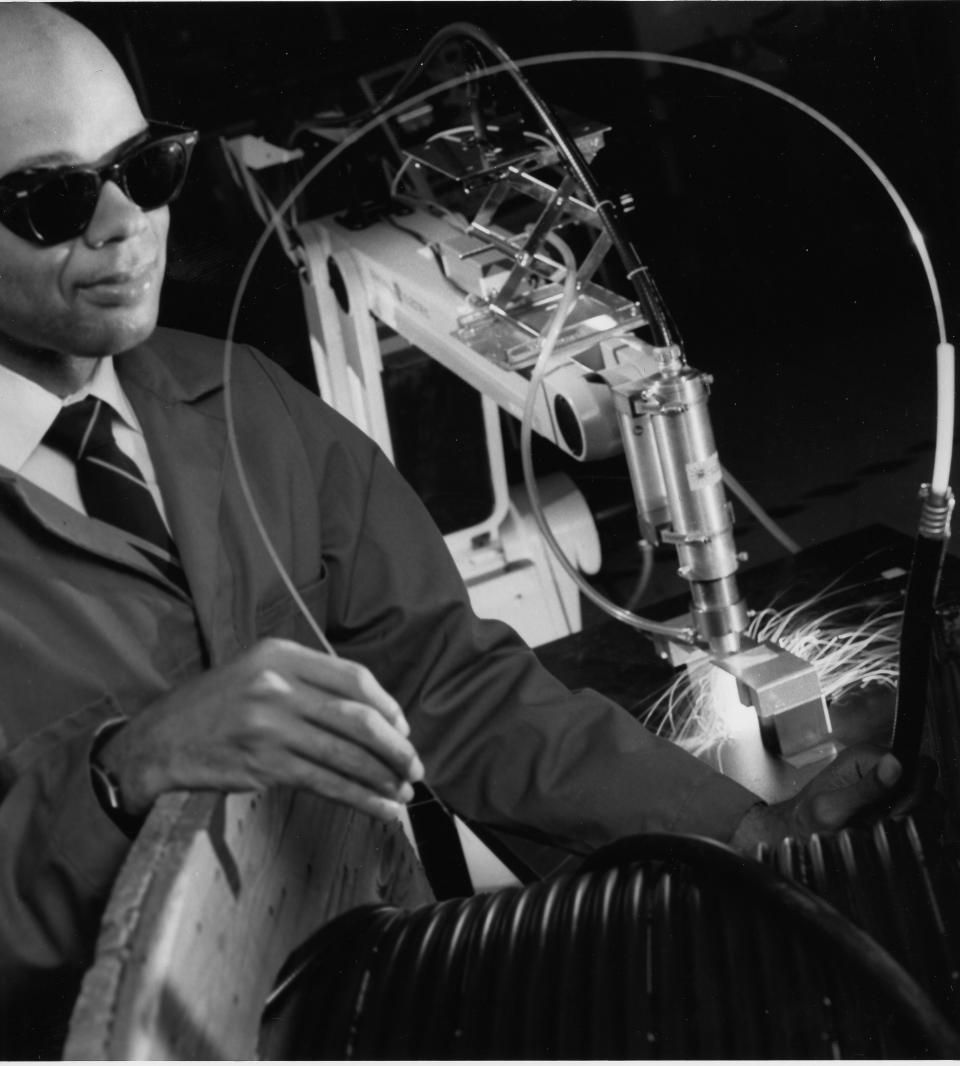
As the executive leader for robotics at GE Global Research, John Lizzi may have one of the coolest jobs at GE. His desk is right next to a classroom-size lab filled with collaborative robots that can safely work next to humans; envelope-like devices that can worm inside a jet engine, inspect it and even fix it; and drones that can keep an eye on wind turbines and other large industrial assets. GE Reports recently visited Lizzi’s lab and talked to him about his favorite robots and the latest developments in the field.