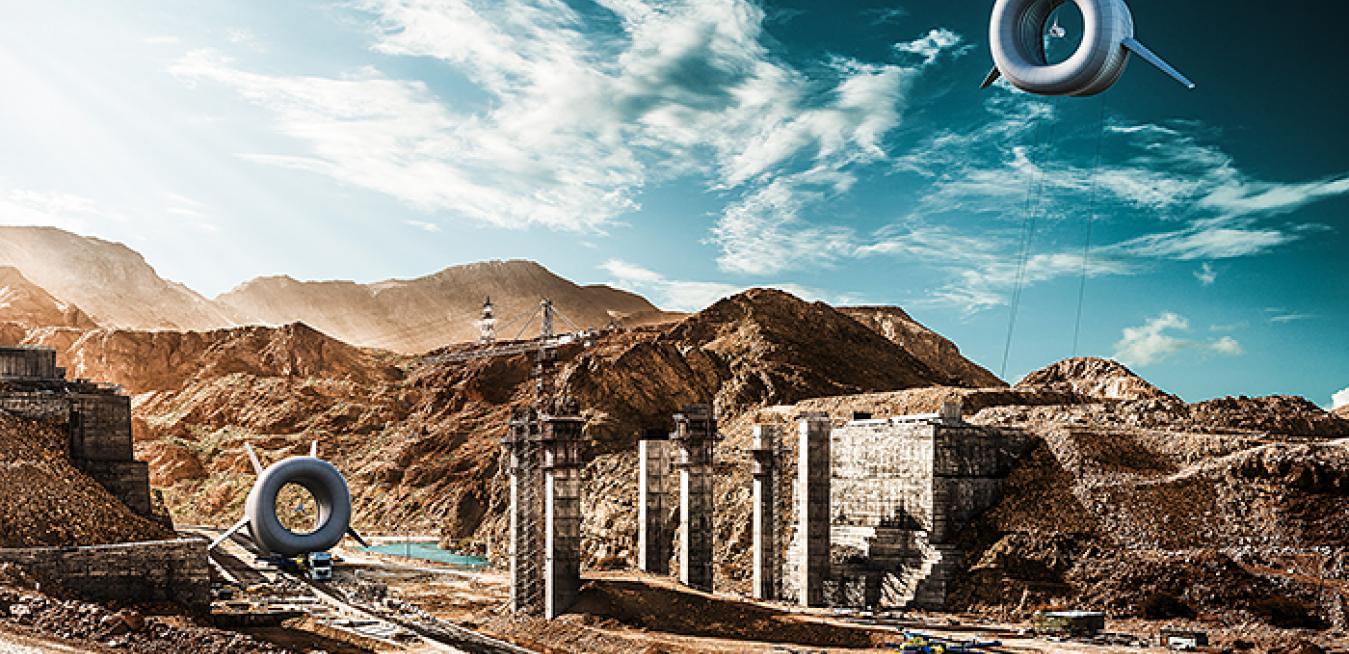
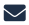
BATs floating 1,000 feet above the earth could hold the secret to providing cheap, quickly installed power to off-grid consumers or disaster-stricken areas.
The BAT, short for “Buoyant Air Turbine,” is essentially a wind turbine in the sky. Developers across the country and around the world are testing various methods of sending these lightweight, high-altitude turbines aloft, using blimps, winged aircraft, and cylindrical balloons to reach sweet-spot heights where operators can harvest the most wind with the least resistance.