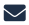
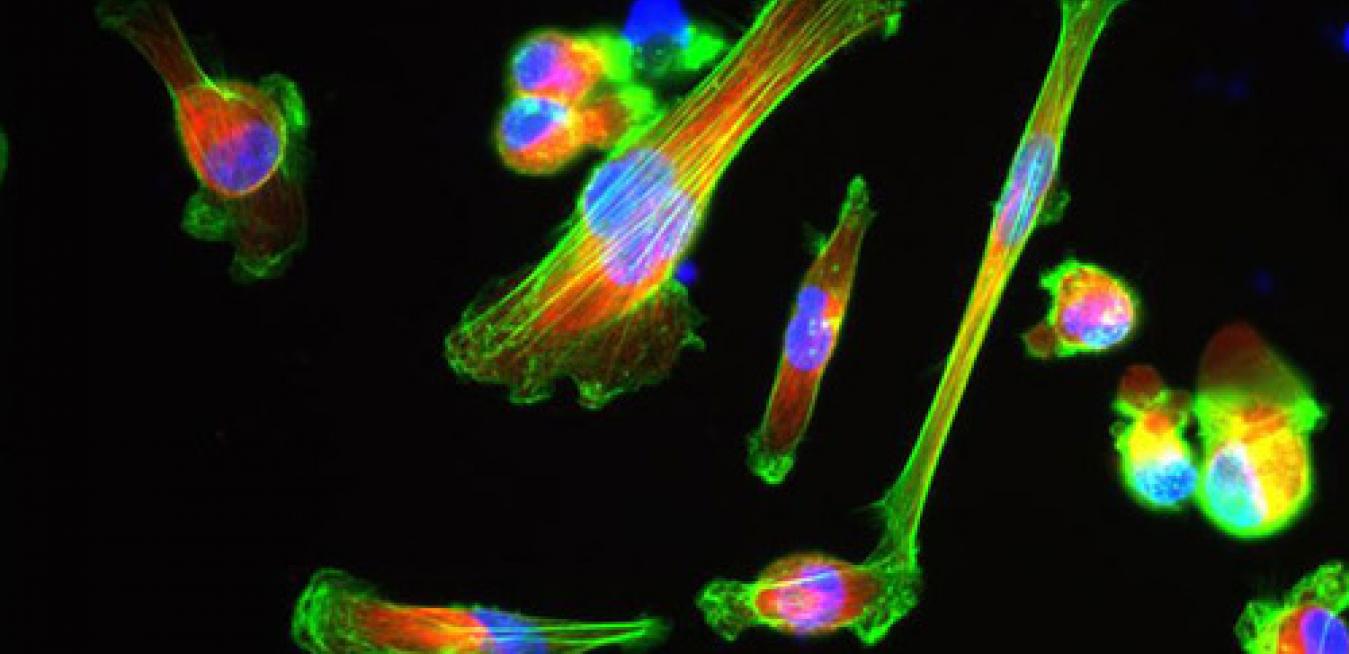
It can be a pain. “Every time I reach for a new slide, I have to take my eyes off the lens and check the forms for that case,” says Ian Cree, professor of pathology at Warwick Medical School in Coventry, UK. “You can get a sore neck from hours at the microscope.”
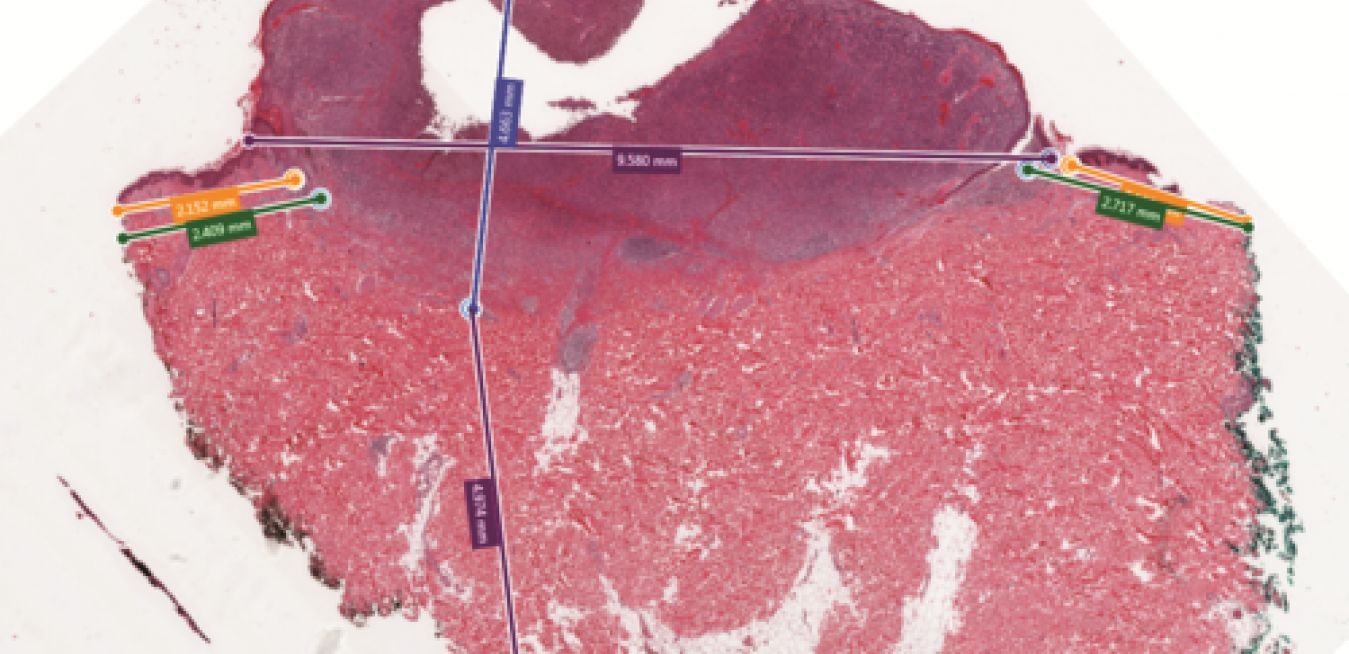
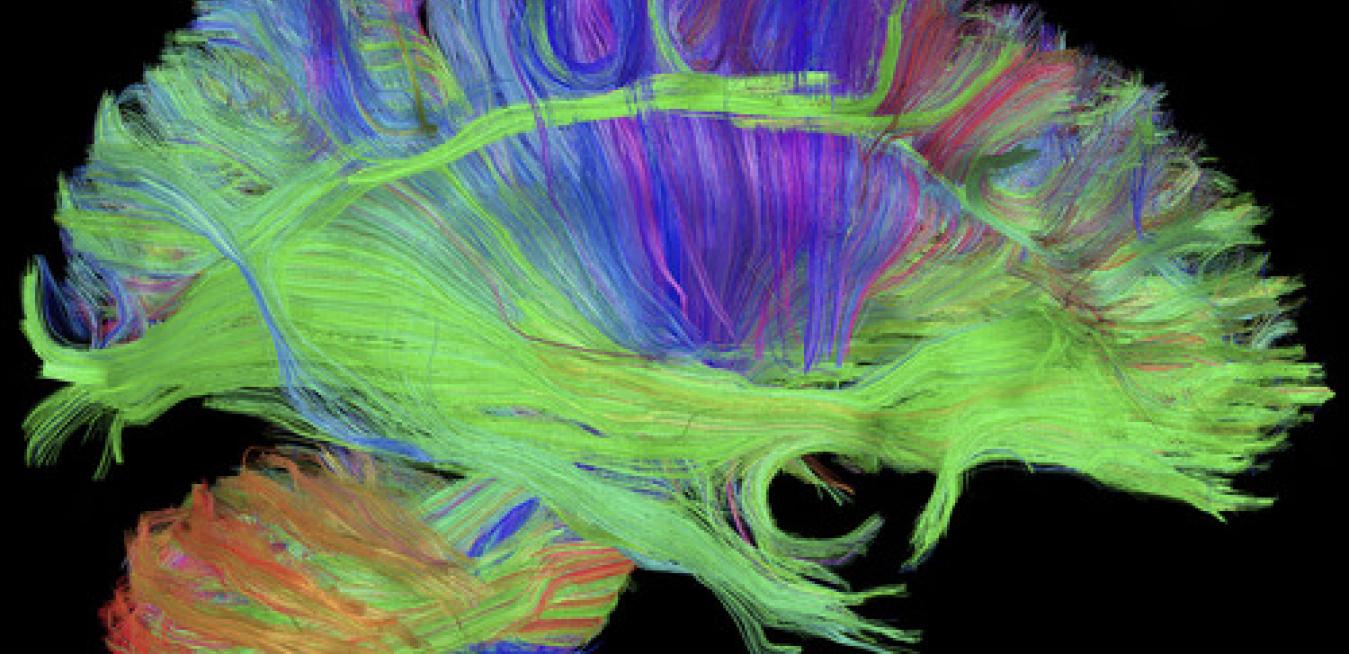
There is no cure for Alzheimer’s disease, no definitive test and no way to prevent it. Yet when asked, an overwhelming number of people around the world say they want to know whether they are at risk. “I was surprised by the consistency and strength of that need,” says Ben Newton, who leads the neurology unit at GE Healthcare Life Sciences. “This strength of feeling is rare for a disease that we cannot treat.”