With each new generation of engine technologies, we’ve travelled faster and safer with less impact on the environment.
It’s been a long, exciting journey since the early days when the wind carried the First Fleet’s eleven ships to Sydney Cove on January 26, 1788.
To recognise their voyage this Australia Day, and the spirit of adventure behind marine engine development, here is a look at the technologies that helped connect the world.
Sailing by steam
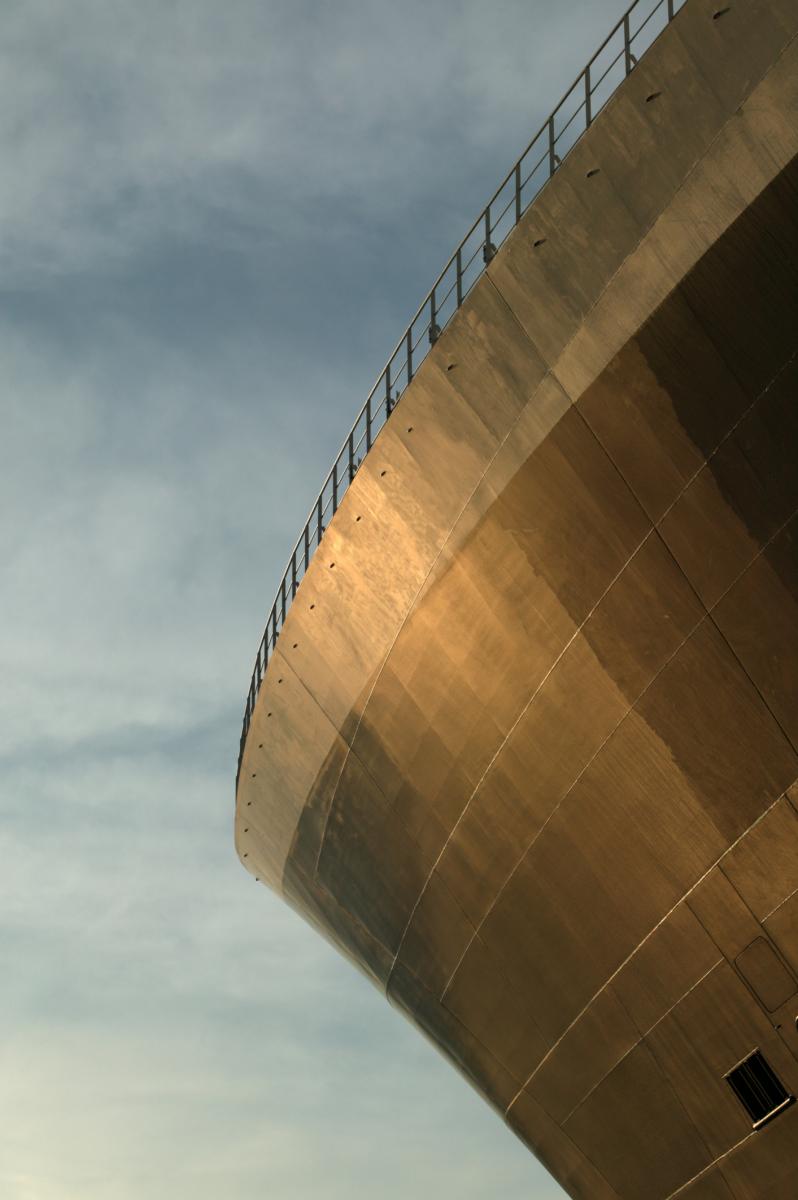 RMS Queen Mary 2, which features a combination of diesel engines, GE gas turbine engines and electric motors.
RMS Queen Mary 2, which features a combination of diesel engines, GE gas turbine engines and electric motors.