GE Research is creating a new platform for innovation by launching a 5G testbed in the Forge Lab at the Niskayuna Research campus. Delivered in partnership with Verizon, GE is leveraging 5G’s next gen speed, scale, reliability, and flexibility to create the industrial devices of tomorrow.
The testbed at GE Research, announced in April, includes Verizon’s 5G Ultra Wideband, with plans to expand to additional 5G technologies in the coming months. By tapping into these 5G capabilities, the teams at GE Research can execute on their vision of creating next generation healthcare, energy, and aviation applications.
Demystifying 5G
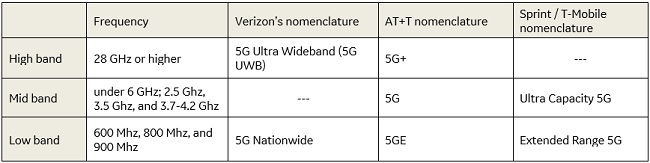
When most people hear the term 5G they don’t realize that the mobile network comprises three different categories: high band, mid band, and low band.
High band 5G uses an ultra-wide millimeter wave spectrum to enable faster network data speeds and reduced lag time. Verizon’s high band network is called 5G Ultra Wideband; AT+T’s is called 5G+.
Mid band 5G, also known as sub-6, is slower than high band but offers more coverage. Verizon doesn’t make a distinction between its high and mid-band networks; AT+T’s is simply called 5G.
Low band 5G is a the more broadly known and available 5G offering. This allows 5G-enabled devices – namely cell phones – to remain on 5G technology when a high-band network isn’t available. Verizon’s low band network is called 5G Nationwide; AT+T’s is called 5GE.
Building a Testbed Starts with Strong Relationships
In the United States, the race to 5G has heated up, and there’s no place better than the GE Research campus in Niskayuna to develop 5G capabilities.
“It was clear there was going to be a major investment in 5G, and we wanted to be part of that conversation,” said SM Hasan, a GE Research engineering leader who supports many of GE’s government projects. Hasan is also GE Research’s 5G mission leader. “We bring decades of technical expertise, a wide range of great partnerships, and technology that spans industries.”
Hasan led the development of a paper for the National Spectrum Consortium detailing 10 technical areas where GE Research can utilize 5G to overcome challenges and/or optimize availability and safety. Active projects like remote patient monitoring, industrial controls, telerobotics, and aircraft asset & operations management could benefit from the near instantaneous response times that 5G enables.
Behind the scenes, Hasan has worked logistics to ensure the 5G rollout meets the expectations of both GE’s IT and the researcher communities. He’s working closely with Eric Tucker, the senior director of enterprise high performance computing and research missions; Christopher Miller, a network operations engineer; and Ben Verschueren, who oversees a number of mission-based teams as growth leader for GE Research’s Forge Lab.
“The Research Center, and the Forge Lab in particular, create a unique opportunity to showcase 5G in multiple industries,” said Eric. “This industry testbed is the culmination of more than a year’s worth of work to build-in the infrastructure that places GE at the cutting edge of 5G technologies.”
5G’s Role in Research
GE Research’s Forge Lab comprises multiple breakout rooms where lab teams carry out their mission-based projects. Many of the rooms are now equipped with 5G antennas, so teams can develop and test products and sensors with the power of 5G.
“Beyond just improved bandwidth and latency, 5G brings a ton of built-in capability, from edge computing to security to virtualization, and many more. Previously we had to build custom solutions for every industrial use case to address these areas, creating complexity to design and limitations to what we could achieve,” said Ben. “It’s exciting to have all of that built-in, enabling us to shift both how we design and reimagine what is possible.”
So, what does a world with 5G look like? In energy, you can imagine renewable energy assets like offshore wind farms wirelessly controlled and monitored in near real-time to improve resiliency and energy output. In healthcare, wireless patient monitoring in the home could become a new normal. Telemedicine opportunities will expand to seamlessly connect patients with top medical experts close to home as well as halfway around the world. Watch this video with Ben to learn more about how 5G will transform industry.
As Ben concludes in the video, “4G to a consumer was what transformed my personal device into something I can use pervasively. 5G is really about industry. Industrial use cases will be the killer apps for 5G.”
For more on 5G, including frequently asked questions, click here.
We're here to solve your toughest problems.






