GE Research Website Timeline








No other company can claim a heritage of innovation as deep and broad as GE Research. From Thomas Edison’s first commercially viable light bulb to the introduction of bioelectronic medicine in healthcare, GE Research has a history of turning research into reality to redefine industries. Our breadth of expertise and experience gives us the ability to disrupt industries with exponential innovations in multiple technical realms. As we remind ourselves of our commitment to progress and research, we continue to leverage our multidisciplinary core capabilities to design and develop the next generation of technology to address the world’s most complex and challenging problems. We’ve encapsulated GE Research’s global impact in five different industries, ranging from healthcare to electronics to aviation. With breakthrough technologies across multiple sectors, GE Research turns cutting-edge research into impactful realities.
1918
GE builds a record-capacity water-wheel generator for Niagara Falls.
1920
The first hydro turbine is built by Neyret Beylier Piccard Pictet (NBPP), the company that later became part of Alstom Energy, which is later acquired by GE.
1922
Niagara orders two generators from GE to replace the original 65,000 kVA unit.
1936
A GE 82,500-kva turbine is first brought online at the Hoover Dam, which would soon become the largest hydropower facility in the world.
1942
The Grand Coulee Dam, with generators made by GE, opens in Washington.
1965
Alstom, whose energy assets were later acquired by GE, optimizes the classic Francis water turbine, increasing output.
1970
Alstom, whose energy assets were later acquired by GE, optimizes the classic Pelton turbine, increasing output.
1984
The Itaipu Dam between Brazil and Paraguay goes online, becoming the world’s largest generator of hydropower to date.
2012
GE is part of a consortium that builds turbines for Three Gorges Dam in China.
2015
GE expands its renewable energy portfolio with the acquisition of Alstom Energy.
2016
GE unveils Digital Hydro Plant technology, which makes hydropower more efficient through automation and data-driven maintenance.
2017
GE launches a brand-new aerating hydro turbine technology.
2018
GE launches a new technology that allows fish to safely pass through hydroelectric power stations.
2007
The J624 Jenbacher high-speed gas engine technology produces more energy more efficiently, providing clean on-site power generation.
2015
The world’s largest and most efficient heavy-duty gas turbine, GE’s HA, is developed using Fastworks and the GE Store of technology.
1939
The world’s first gas turbine for electricity production is created.
1949
GE ships the United States’ first gas turbine for electricity production to Oklahoma Gas & Electric.
1955
GE provides Union Pacific with 8,500 horsepower gas-turbine electric locomotives.
1975
GE’s turbines are used by a US naval destroyer for the first time.
1990
The world’s first F-class turbine begins operation and is still running to this day.
2003
GE’s H System gas turbine test operations start.
2014
GE introduce s the flagship HA gas turbine, the fastest fleet of heavy-duty gas turbines in the world.
2015
GE finishes the first production unit of the 9HA Gas Turbine.
2016
GE’s HA turbine is recognized by Guinness World Records with an efficiency of up to 62.
2017
GE earns another Guinness World Record for efficiency.
1941
GE builds the first U.
1949
GE introduces what will become the world’s most-produced jet engine in history, the J47.
1971
GE moves into the civil market for high-bypass turbofan engines, making the CF6 the most popular engine family for wide-body aircraft, including Air Force One.
1999
With more than 115,000 lbs.
2010
The next-generation jet engine with ceramic components and 3-D printed parts takes its first flight.
1919
The GE supercharger makes its maiden flight over McCook Field in Dayton, Ohio.
1921
Lt. John Macready sets a new world altitude record with a GE Supercharger.
1929
GE develops the innovative magneto compass.
1937
Howard Hughes sets a transcontinental air record.
1941
GE builds the first US jet engine, the I-A.
1943
US military aircraft equipped with approximately 100,000 GE turbo superchargers for the war effort.
1944
The US Army Air Corps flies its first operational jet fighter, powered by a GE J33.
1949
GE introduces the J47, which becomes the world’s most-produced jet engine.
1954
GE’s Small Aircraft Engine Division in Lynn, Massachusetts, designs the T58 “baby gas turbine.”
1957
GE develops the J93, the first engine to operate at three times the speed of sound.
1965
GE unveils the TF39 turbofan.
1970
GE’s first afterburning turbofan, the F101, is selected to power the US Air Force’s new B-1 Bomber.
1978
GE delivers its first T700 to power Sikorsky Black Hawk helicopters.
1982
The CFM56 Engine is introduced.
2002
The GE90-115B engine sets a world record for thrust.
2004
GE begins development of the GEnx engine.
2008
GE and Safran Aircraft Engines unveil the LEAP-X next-generation engine program.
2013
Boeing selects the GE9X as the sole engine for its 777X commercial planes.
2018
The initial architecture of GE’s Affinity, the first commercial supersonic engine in 55 years, is introduced.
1882
The Edison Electric Illuminating Company turns electricity into a commodity, constructing the first central power station in New York City.
1957
Continuing to pioneer in the field of energy generation, GE opens the world’s first licensed nuclear power plant.
1882
Thomas Edison and his team develop the first dynamos capable of powering neighborhood-wide lighting systems.
1889
Elihu Thomson invents the integrating wattmeter.
1905
GE creates Ebasco (Electric Bond and Share Company) Systems.
1957
Shippingport Atomic Power Station becomes the world’s first commercial nuclear power plant.
1972
World’s first commercial thyristor High Voltage Direct Current scheme (HVDC) debuts at Eel River, Canada.
1982
GE introduces the P4A, the first digital relay, signifying a technological leap forward in electrical protection.
2005
GE introduces the first wide-area protection schemes.
2014
GE releases Green Gas for Grid (or g3).
2015
GE improves performance of power grids through its acquisition of Alstom Energy.
2002
GE continues its focus on sustainable energy, entering the wind power business.
2002
GE enters the wind business through the acquisition of Enron’s wind assets.
2008
Shepherd’s Flat Wind Farm in Oregon uses 338 of GE’s 2.5 MW wind turbines to generate 2,000 GWh annually.
2015
GE enters the offshore renewable energy industry through the Alstom Energy acquisition.
2016
The Block Island Wind Farm near Rhode Island becomes the first offshore wind farm to go online in the US.
2017
GE completes acquisition of LM Wind Power, a Denmark-based maker of rotor blades.
2018
GE launches its largest onshore turbine to date, which features unique two-piece blades.
2019
The first Haliade-X 12 MW wind turbine prototype is installed in Maasvlakte-Rotterdam.
2015
GE combines its deep base of industrial knowledge with software to create digital models of physical assets and processes to deliver business outcomes for customers.
1986
GE and Fanuc combine to create GE Fanuc Automation Corporation, which manufactures programmable logic controllers—one of the fundamental building blocks of what’s come to be known as the Industrial Internet of Things.
1991
GE introduces the first digital control system for utility networks.
1993
GE launches the first optical multiplexer for high speed utility communications of voice, video, and data.
1998
GE launches first protection relays to support Ethernet and peer-to-peer communications.
2001
GE Measurement and Control is established.
2007
GE launches the Multilin D90plus, the world’s fastest sub-cycle distance protection relay.
2008
GE introduces the innovative HardFiber process bus solution.
2015
GE opens digital collaboration centers in Dubai, Shanghai, and Paris.
2016
GE Aviation opens its digital collaboration center in Austin, Texas, with launch customer Qantas Airways.
2018
GE Aviation's accelerator in Washington DC launches.
2019
GE Aviation announces its Aviation Asset Performance Management (APM) solution.
1895
GE puts electricity to work on a large scale in 96-ton electric locomotives.
1906
The world’s first voice radio broadcast is made possible by Ernst Frederick Werner Alexanderson’s high-frequency alternator.
1906
The world’s first voice radio broadcast is made possible by Ernst Frederick Werner Alexanderson’s high-frequency alternator.
1910
GE improves life in the kitchen with the first electric range.
1914
Charles Steinmetz develops an electric vehicle, which is able to reach a top speed of 40 miles per hour, powered by 14 six-volt batteries.
1927
The first home television reception takes place in Schenectady, NY with a signal from GE’s WGY.
2003
GE introduces the new fuel-efficient Evolution Series locomotives.
1930
GE develops moldable plastic, a foundational technology in the advance of modern mass production.
1944
GE introduces silicone for commercial use.
1962
GE researchers achieve two laser breakthroughs that will have profound effects on manufacturing.
1995
GE revolutionizes its manufacturing by adopting Six Sigma.
2012
GE acquires 3D-printing pioneer Morris Technologies, whose sophisticated techniques allow the creation of lightweight, streamlined versions of complex items like fuel nozzles for jet engines.
2015
GE introduces the Catalyst turboprop engine.
2018
GE’s Distributed Power facility in Jenbach, Austria, is named Factory of the Year by the trade magazine Produktion.
1983
GE scientists develop the Signa Magnetic Resonance Imaging System, which produces images of “soft” tissues difficult to image by X-ray methods.
1896
GE's Elihu Thomson builds electrical equipment for the production of X-rays.
1913
GE researcher William Coolidge develops the hot-cathode, high-vacuum X-ray tube.
1932
Associate Director of GE Research Laboratory Irving Langmuir wins the Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
1959
The world’s first commercial size exclusion chromatography resin, Sephadex, launches.
1974
The first non-ionic X-ray contrast media is introduced.
1978
The first routine total-body computed tomography (CT) scanner is made widely available.
1983
The first high-field 1.5T magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner is introduced.
1999
The first commercial SPECT/CT combination designed as a single unit is introduced.
2000
The first 4D high-res ultrasound system for women’s health enables visualization of fetal movement in utero.
2011
The first single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) imaging agent is released.
2012
The world’s first modular biopharmaceutical facility, KUBio™, is opened.
2015
The first NASA-style clinical hospital “command center” launches.
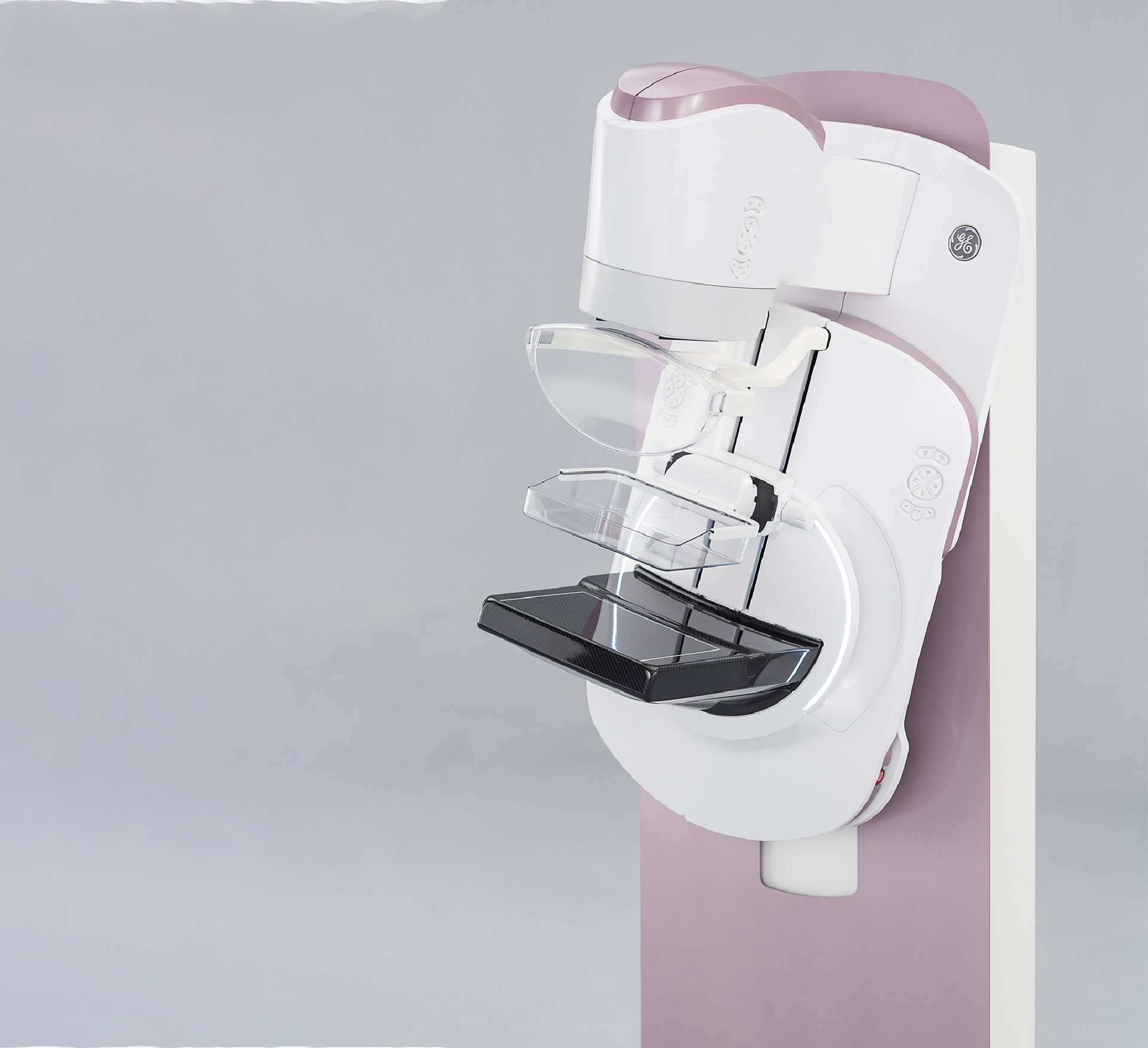
2016
A mammography system featuring the world’s first patient-assisted compression remote control debuts.
2017
Cell therapy enterprise offering launches with the acquisition of Asymptote Limited.
2019
The first deep learning-based CT image reconstruction technology gains FDA clearance.
1879
Edison invents the first commercially practical incandescent lamp.
1896
A rich tradition of GE breakthroughs in medical imaging begins with the demonstration of stereoscopic Roentgen pictures.
1908
Developed by William D.
1912
Drs.
1920
GE develops a new X-ray machine suitable for dental and portable use.
1932
Irving Langmuir becomes the first US industrial scientist to win the Nobel Prize, received for his research in the field of surface chemistry.
1938
GE invents the first practical low-pressure discharge lamp to provide white light.
1939
Katharine B.
1940
GE invents a new silicones chemistry, marking the start of the silicones business.
1953
Daniel W.
1955
GE Research Laboratory announces the invention of the first reproducible process for making industrial-use diamonds.
1962
The laser light is invented, making possible many of today’s most popular technologies such as DVD players.
1969
GE supplies a variety of technologies for the first landing on the moon, including engineering support, test facilities, and the silicone for Neil Armstrong’s boots.
1992
GE builds the Mars Observer for NASA, which will study Martian geology and climate while mapping the planet’s surface.
1998
This scanner is the first to capture multiple images simultaneously and is six times faster than traditional single-slice scanners.
2004
GE launches the UltraScanTM Duo, the first liquid pipeline inspection tool to utilize Phased Array Ultrasound Technology.
2009
Vscan, a handheld, pocket-sized ultrasound technology, helps doctors deliver expanded care to more people, including in rural regions.
2010
The WattStation charges electric vehicles at home or on the road, with an upgradable design that allows customers to stay current with the latest technology.
2013
GE is developing the next evolution of power devices with Silicon Carbide technology.
1879
Thomas Edison and his researchers create a lightbulb filament that can incandesce for 1,200 hours.
1908
GE Research Lab’s William Coolidge creates the tungsten filament.
1927
Coolidge develops the first enclosed X-ray source, the inspiration for many X-ray devices that are used to determine the physical makeup of materials.
1939
GE researcher Katharine Blodgett invents non-reflective glass.
1942
Researchers from GE and RCA demonstrate the first commercial TEM (transmission electron microscope).
1947
Synchrotron radiation is first demonstrated at General Electric Research Laboratory.
1953
GE chemist Dr. Daniel Fox is the co-discoverer of polycarbonate resin.
1955
GE researcher H. Tracy Hall creates the first synthetic diamonds.
1969
Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin walk on the moon wearing boots made from silicon rubber developed by GE.
1995
GE introduces the first jet engine to include components made of lightweight carbon fiber composites.
2017
The LEAP jet engine is the first widely deployed product to feature ceramic matrix composites.