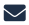
The Number Of Galaxies Just Jumped Tenfold To 2 Trillion
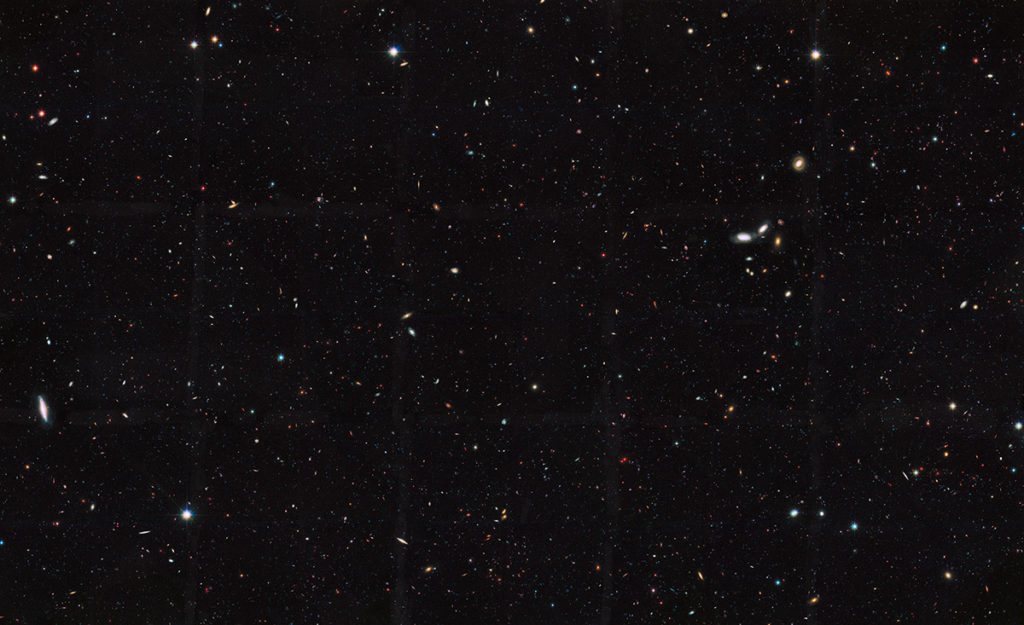 This Hubble Space Telescope view reveals thousands of galaxies stretching back into time across billions of light-years of space. The image covers a portion of a large galaxy census called the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey (GOODS). Image credit: NASA. Top image credit: Getty Images.
This Hubble Space Telescope view reveals thousands of galaxies stretching back into time across billions of light-years of space. The image covers a portion of a large galaxy census called the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey (GOODS). Image credit: NASA. Top image credit: Getty Images.When Carl Sagan said “the total number of stars in the universe [was] greater than all the grains of sand on all the beaches of the planet Earth,” he made millions of people look up. He may have also committed the biggest rounding error in history. Astronomers imaging the deep space with the Hubble Space Telescope just reported that the observable universe holds 10 times as many galaxies as previously thought, boosting their number from 200 billion to 2 trillion. That puts the number of stars to 700 sextillion — 700 followed by 21 zeroes, Gizmodo reported. Compare that with the number of sand grains on Earth — 7.5 quintillion, or 75 followed by 17 zeroes — according to an NPR account. The vast majority of galaxies still remain too faint to see even with our best instruments. "It boggles the mind that over 90 percent of the galaxies in the universe have yet to be studied,” said Christopher Conselice of the University of Nottingham, U.K., who led the team. “Who knows what interesting properties we will find when we discover these galaxies with future generations of telescopes?” NASA is planning to launch the James Webb Space Telescope, which can see infrared light, in October 2018.
Scientists Make A Paralyzed Man Feel With A Mind-Controlled Robotic Arm
[embed width="800"]https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=L1bO-29FhMU[/embed]
People have been able to control robotic arms with their minds for a while now, but never before could they feel what the robot was touching. Now researchers at the University of Pittsburgh and UPMC have connected the brain of Nathan Copeland, a 28-year-old man paralyzed in a motorcycle accident, to a brain-computer interface that made him “experience the sensation of touch though a robotic arm that he controls with his brain.” They first imaged his brain and implanted the electrodes in the parts of the brain that correspond to feelings in each of his fingers and his palm. Then the team connected the brain to a mind-controlled robotic arm. “I can feel just about every finger — it’s a really weird sensation,” Copeland said about a month after surgery. “Sometimes it feels electrical and sometimes its pressure, but for the most part, I can tell most of the fingers with definite precision. It feels like my fingers are getting touched or pushed.” Said Robert Gaunt, assistant professor of physical medicine and rehabilitation: “The ultimate goal is to create a system which moves and feels just like a natural arm would. We have a long way to go to get there, but this is a great start.”
2030 Space Odyssey
 “Getting to Mars will require continued cooperation between government and private innovators, and we're already well on our way,” says President Obama. Image credit: Getty Images.
“Getting to Mars will require continued cooperation between government and private innovators, and we're already well on our way,” says President Obama. Image credit: Getty Images. U.S. President Barack Obama just announced a “clear goal vital to the next chapter of America’s story in space”: to send humans to Mars by 2030 and return them safely to Earth. “Getting to Mars will require continued cooperation between government and private innovators, and we're already well on our way,” he wrote in a column published by CNN. “Within the next two years, private companies will for the first time send astronauts to the International Space Station. The next step is to reach beyond the bounds of Earth's orbit. I'm excited to announce that we are working with our commercial partners to build new habitats that can sustain and transport astronauts on long-duration missions in deep space. These missions will teach us how humans can live far from Earth — something we'll need for the long journey to Mars.”
This Video Induces Hallucinations In Healthy People. It Could Lead To Parkinson’s Treatments
Researchers at the University of New South Wales in Australia have created a video that induces visual hallucinations in healthy people. They want to use it to study how hallucinations affect visual perception and find new treatments for people with Parkinson’s disease. “We have known for more than 100 years that flickering light can cause almost anyone to experience a hallucination,” said Joel Pearson, associate professor at the UNSW’s School of Psychology. “However, the unpredictability, complexity and personal nature of these hallucinations make them difficult to measure scientifically.” Said Pearson: “With our technique we get rid of the unpredictability. People don't see windmills, lines, or different colors; they just hallucinate grey blobs. Once the hallucination is stable like this, with just the blobs, we can start to objectively investigate the underlying mechanisms.” You can watch the video below. The university recommended that “anyone with a history of migraines, epilepsy or psychiatric disorders” should refrain from watching it.
[embed width="800"]https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SJNO-HnPq6k[/embed]
The Naked Mole Rat Can Stand The Heat
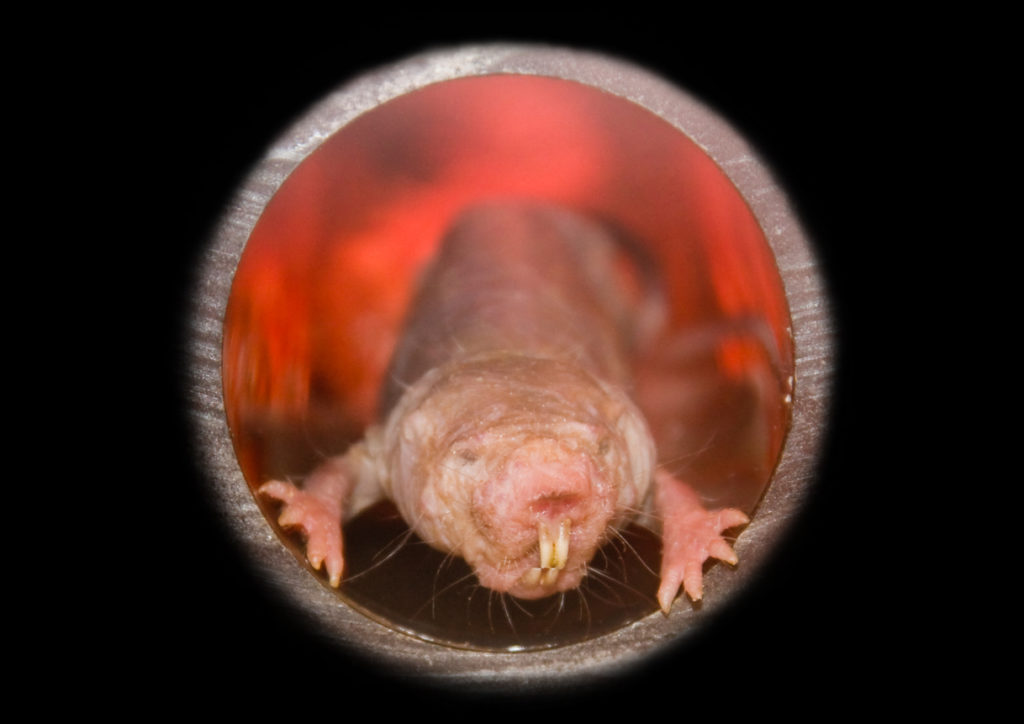 Naked mole rats "have the lowest metabolic rate of any mammal. Evolution has shut down everything that is not absolutely necessary — including extra nerve receptors," says Gary Lewin. Image credit: Getty Images
Naked mole rats "have the lowest metabolic rate of any mammal. Evolution has shut down everything that is not absolutely necessary — including extra nerve receptors," says Gary Lewin. Image credit: Getty ImagesAfrican naked mole rats aren’t pretty to look at, but in many other ways they are amazing animals. Besides living for more than three decades — this makes them Methuselahs among rodents — and being impervious to cancer, they can’t feel pain caused by heat. Scientists in Germany now figured out why: a small change in a sensory receptor. "We think evolution has selected for this tweak just subtly enough so that the pain signaling becomes non-functional, but not strong enough that it becomes a danger for the animal," Gary R. Lewin, a professor at the Max-Delbruck Center for Molecular Medicine in Berlin, told the journal Cell Science. The team believes their high tolerance to heat helps them survive in crowded underground colonies. "They live in desert regions underground, and they have to do a lot of work to get their food," Lewin said. "They have the lowest metabolic rate of any mammal. Evolution has shut down everything that is not absolutely necessary — including extra nerve receptors."