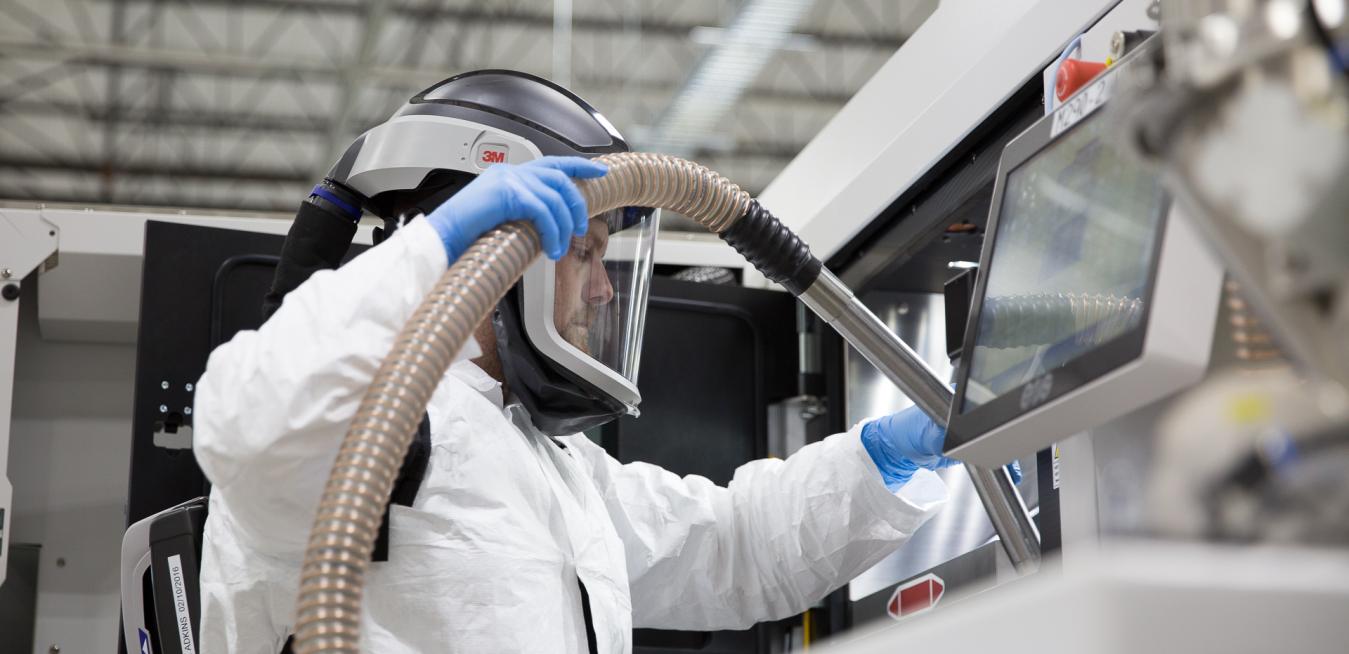
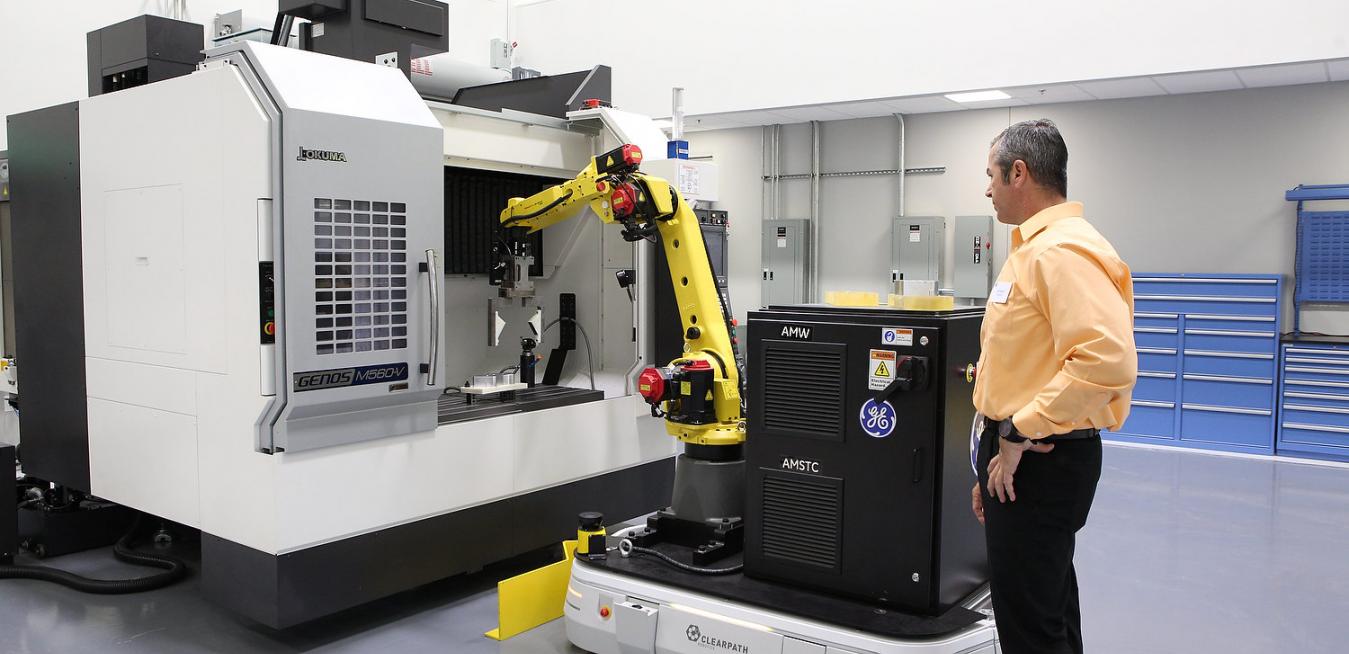
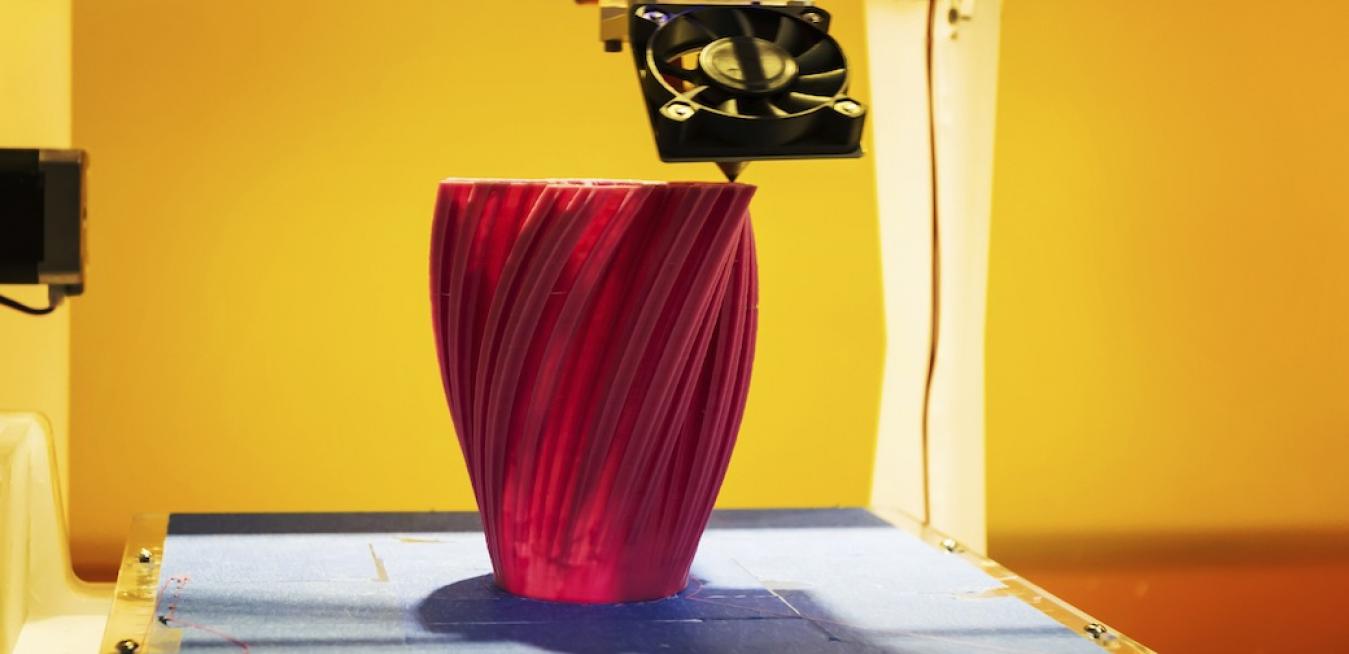
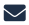
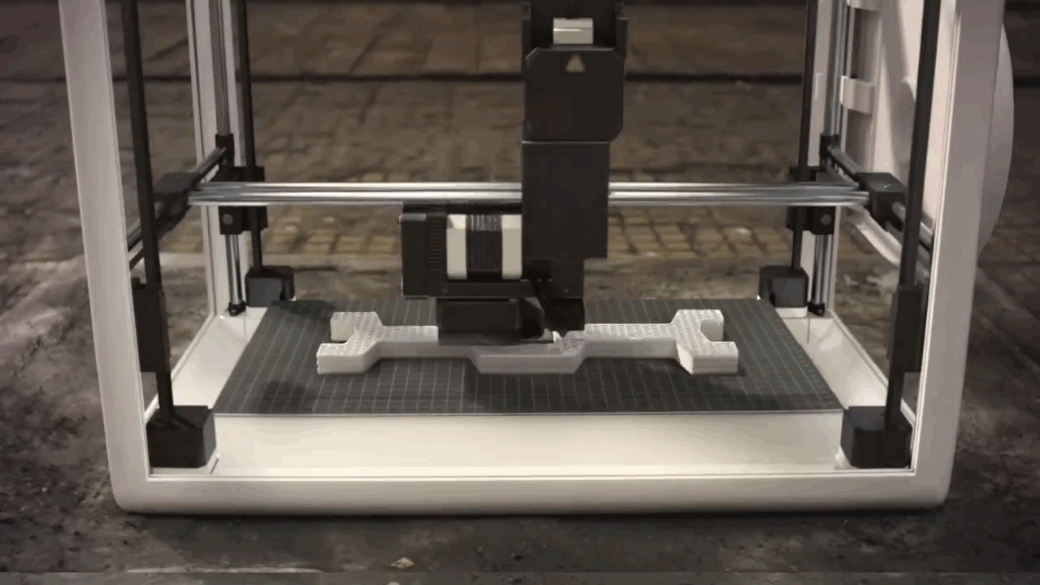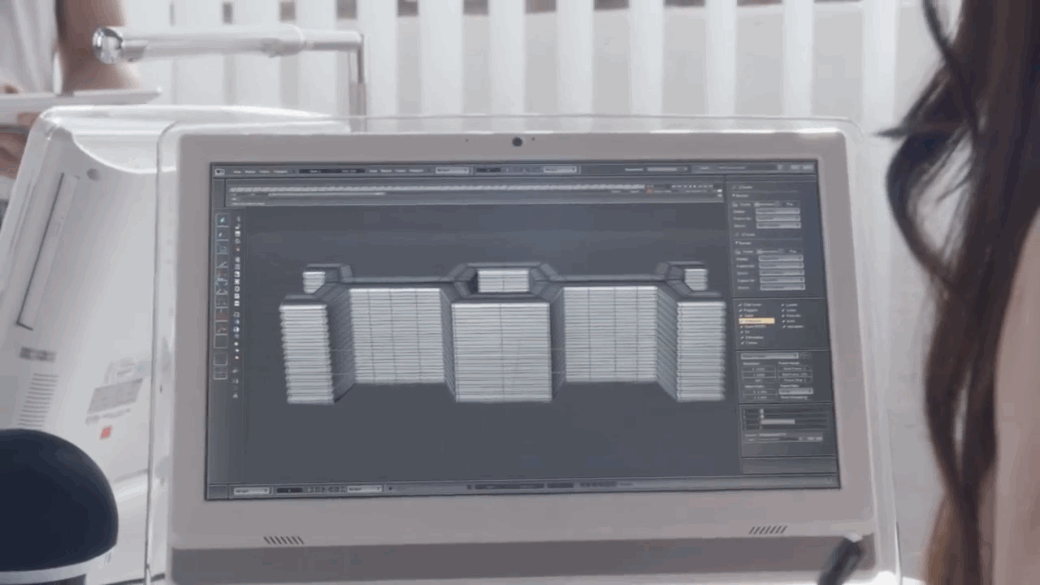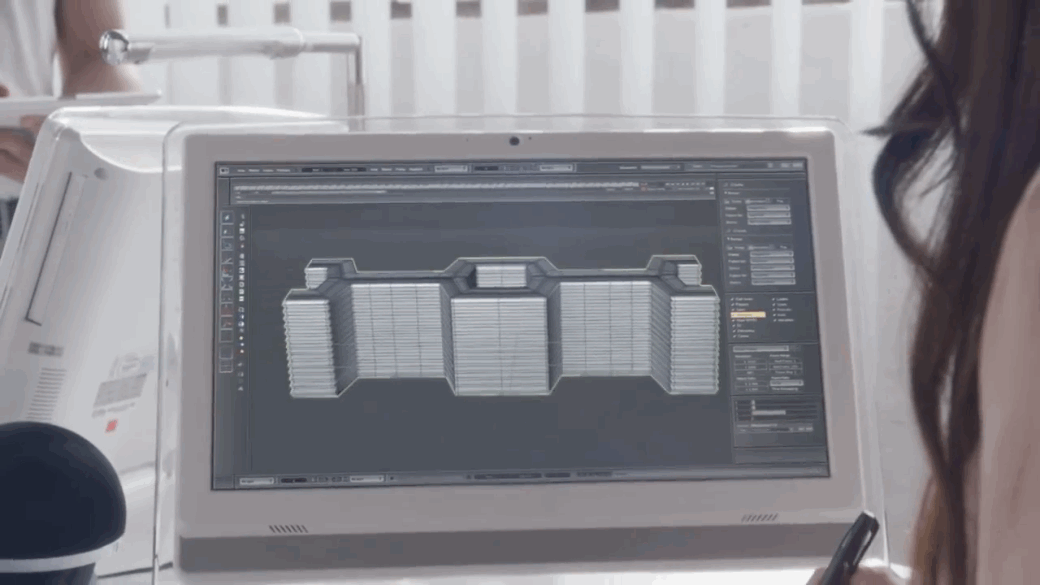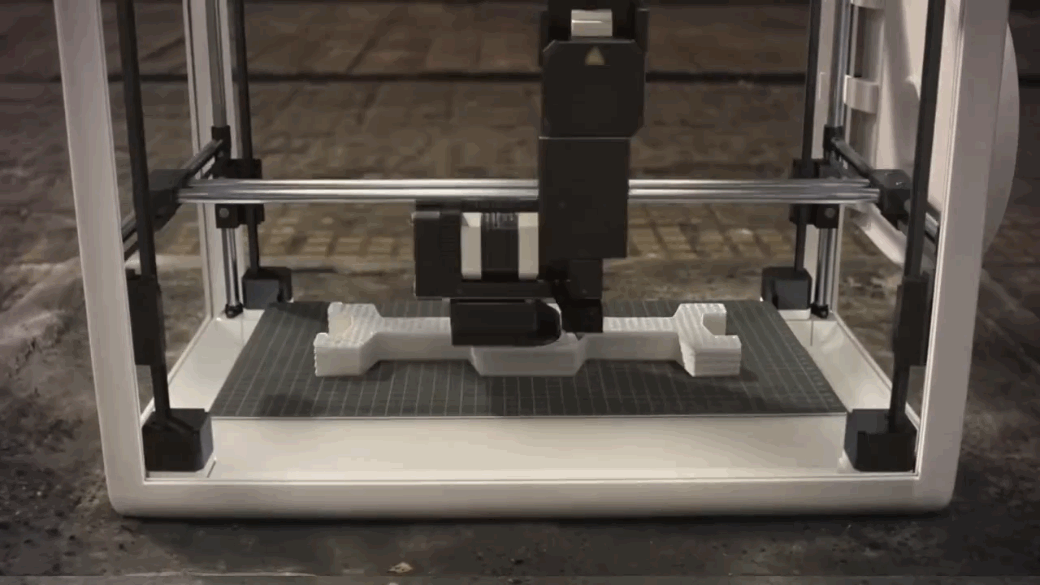
The 4th Industrial Revolution is ushering in a new era in manufacturing by merging hardware and software and reimagining how products are designed, made and serviced. Advanced manufacturing has profound implications for the future of work, as well.
By embracing “bottom-up” innovation, the U.S. government can help advanced manufacturing respond to the speed and complexity of technological change.
Gaining a national edge in the advanced manufacturing space typically isn’t a “top down” process, especially given the speed of technological change. Given that, one of the great strengths of the Obama administration’s National Network for Manufacturing Institutes (NNMI) initiative has been its vision of competitive, “bottom up” project selection and governance.
In this era of hyperconnectivity, transformation is happening faster and impacting every industry. To thrive in this environment, you need to understand these five things.
Someday, we will look back and realize that we live in one of the most fascinating periods in history, with technology having entered a new era of what I call "hyperconnectivity" — where the rate of change is accelerating in nearly every industry.
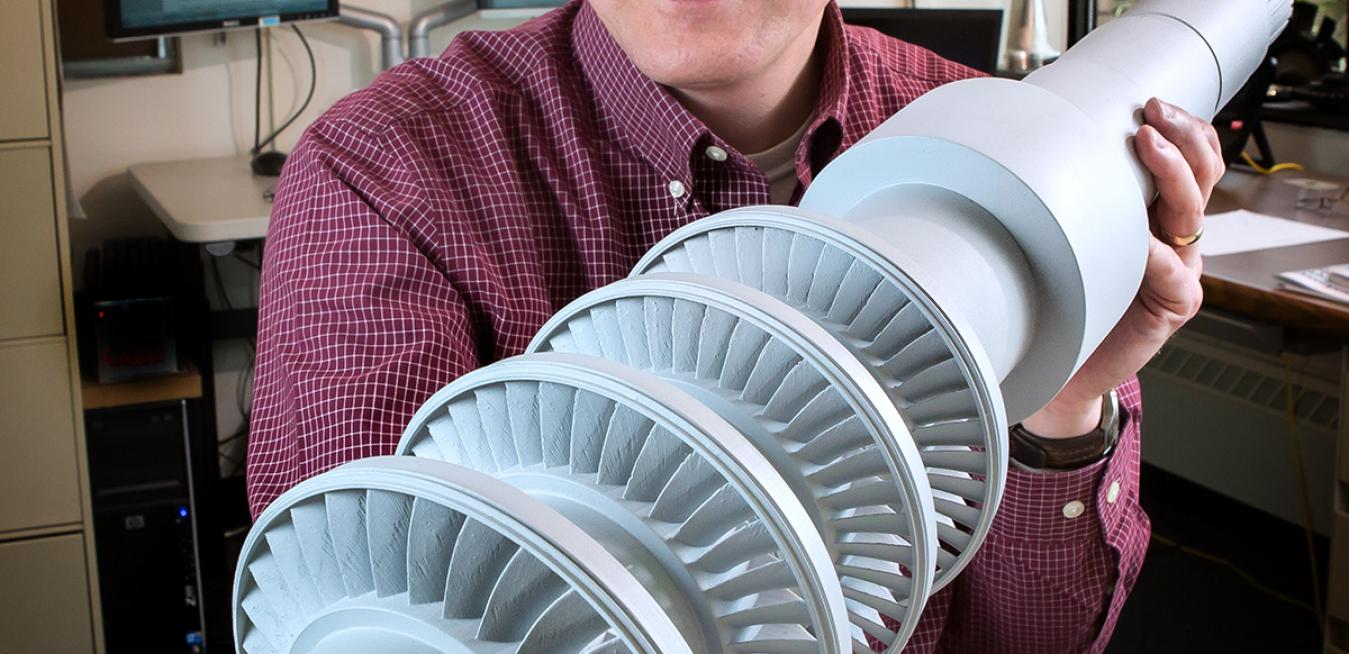
Though small in stature, the turbine in the photos could contribute to solving some of the world’s biggest energy challenges, not to mention powering an entire town, says Doug Hofer, a steam turbine specialist at GE Global Research.
Amid global economic uncertainty, here are three levers for topline growth.
Not a day goes by without news about a slowdown in the world economy. Yet paradoxically, a recent Pricewaterhouse survey revealed that while 70 percent of global executives said it is more difficult to find profitable growth opportunities now than 10 years ago, 74 percent also said there are more profitable growth opportunities now a decade ago.
A 3D-Printed Invisibility Cloak?
The digitization of manufacturing is transforming entire industries. Here are five takeaways from a workshop on how U.S. regional economies can support the development of an ecosystem that brings together hardware and software.
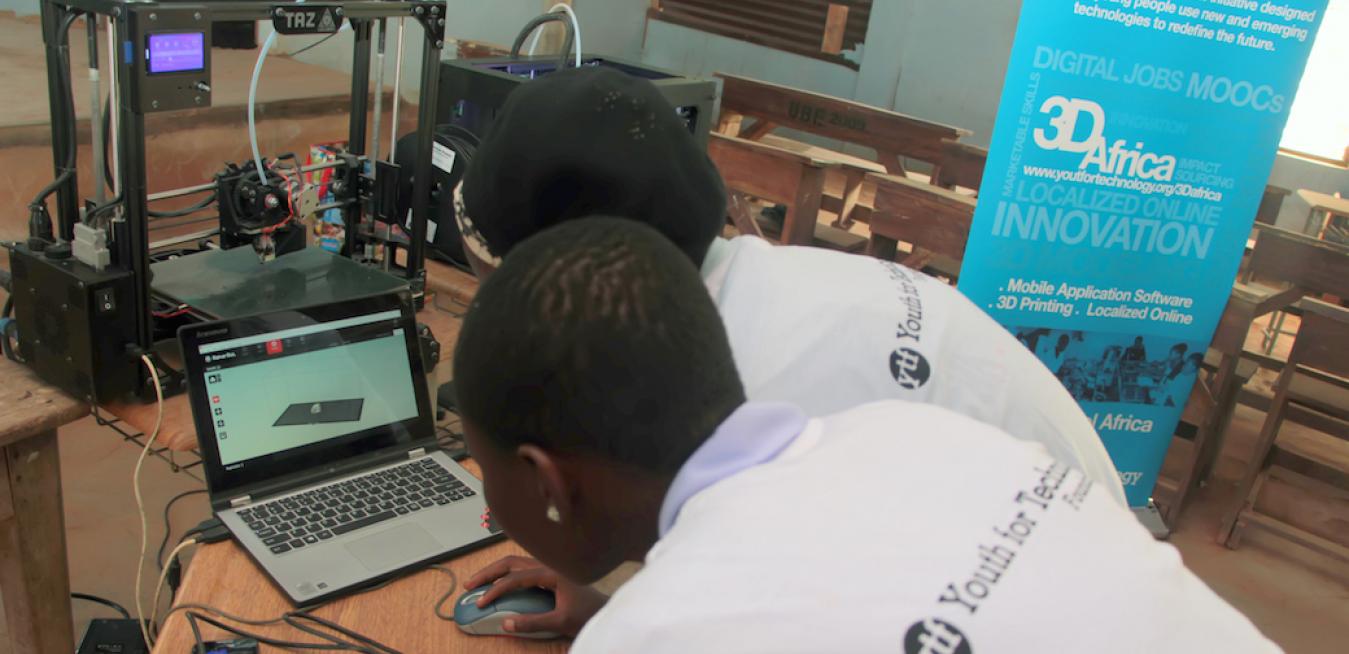
Africa’s young innovators can leapfrog into the digital revolution with the right tools and training.
The 4th Industrial Revolution is driven by newer technologies, such as 3D printing, that are changing industrial processes by accelerating them and making them more flexible. With the right tools and training, young innovators in Africa have the opportunity to skip the second industrial revolution — traditional mass production — and leapfrog straight to digital manufacturing. This, in turn, can provide them with a path out of poverty.