South East Asia countries map on a globe
The Trans-Pacific Partnership Agreement (TPPA) has been ten years in development and is so shrouded in the tightly wound cogs of national secrecy that it’s acquired an almost legendary aura of mystery.
The deal took a major step forward this week with the signing of a TPPA agreement in Atlanta, USA. But with the full terms yet to be revealed, what do we really know about the TPPA? And what does it mean for ASEAN?
What is it?
The emerging Age of Gas, the rise of distributed power and technological innovation will accelerate the adoption of fuel cells into the global energy landscape over the next decade.
The future of power is now under development and it is packaged in stacks of fuel cells. As the world’s energy needs increase, and calls for sustainability continue to rise, a number of forces are converging to expedite the adoption of fuel cells into the global energy mix.
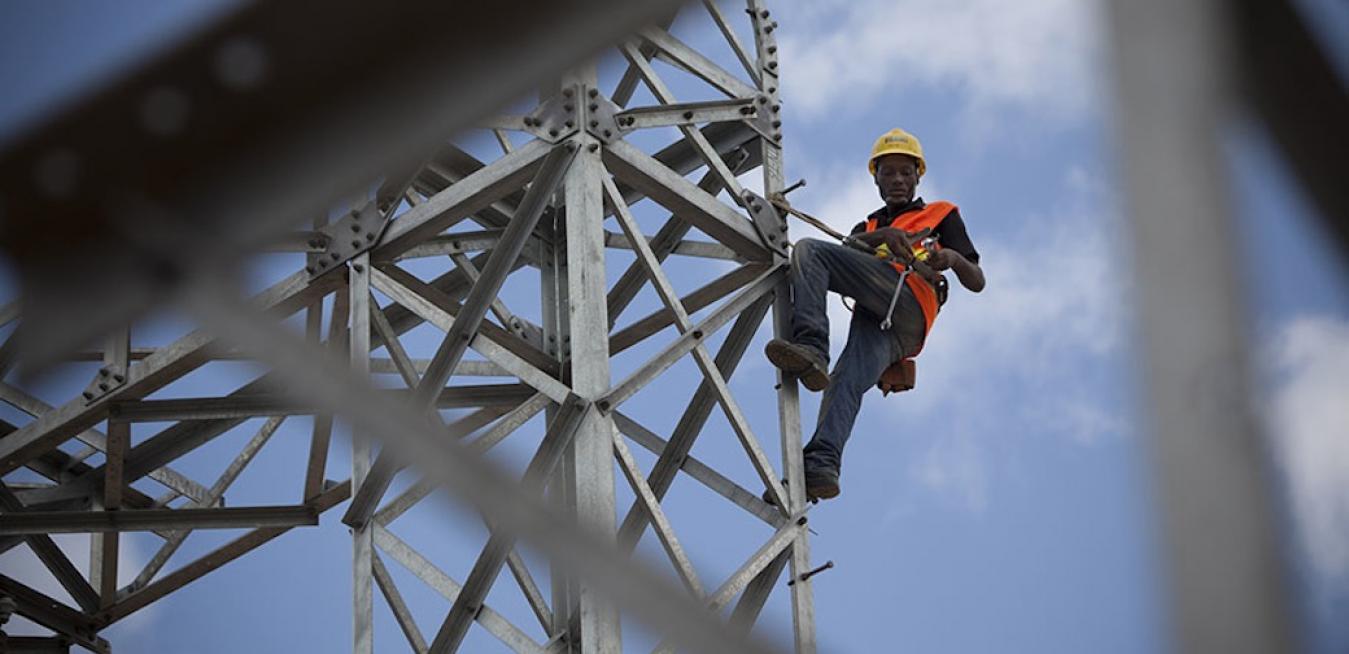
Coal may have its critics, but Japan is demonstrating that the fossil fuel can have a role to play in sustainable economic growth.
Few countries in the world face the energy security challenges of Japan. With virtually no domestic energy resources to speak of — its large methane hydrate resources being decades away from development — Japan has had to rely on imported fuel for almost all of its energy needs.